IL-33 targeting attenuates intestinal mucositis and enhances effective tumor chemotherapy in mice
- PMID: 24424522
- PMCID: PMC4077764
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2013.124
IL-33 targeting attenuates intestinal mucositis and enhances effective tumor chemotherapy in mice
Abstract
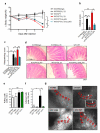
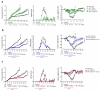
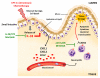
Intestinal damage and severe diarrhea are serious side effects of cancer chemotherapy and constrain the usage of most such therapies. Here we show that interleukin-33 (IL-33) mediates the severe intestinal mucositis in mice treated with irinotecan (CPT-11), a commonly used cancer chemotherapeutic agent. Systemic CPT-11 administration led to severe mucosal damage, diarrhea, and body weight loss concomitant with the induction of IL-33 in the small intestine (SI). This mucositis was markedly reduced in mice deficient in the IL-33R (ST2(-/-)). Moreover, recombinant IL-33 exacerbated the CPT-11-induced mucositis, whereas IL-33 blockade with anti-IL-33 antibody or soluble ST2 markedly attenuated the disease. CPT-11 treatment increased neutrophil accumulation in the SI and adhesion to mesenteric veins. Supernatants from SI explants treated with CPT-11 enhanced transmigration of neutrophils in vitro in an IL-33-, CXCL1/2-, and CXCR2-dependent manner. Importantly, IL-33 blockade reduced mucositis and enabled prolonged CPT-11 treatment of ectopic CT26 colon carcinoma, leading to a beneficial outcome of the chemotherapy. These results suggest that inhibition of the IL-33/ST2 pathway may represent a novel approach to limit mucositis and thus improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Figures




References
-
- Sonis ST. The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(4):277–284. - PubMed
-
- Sonis ST. A biological approach to mucositis. J Support Oncol. 2004;2(1):21–32. discussion 35-26. - PubMed
-
- Mathijssen RH, van Alphen RJ, Verweij J, Loos WJ, Nooter K, Stoter G, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11) Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7(8):2182–2194. - PubMed
-
- Hebbar M, Ychou M, Ducreux M. Current place of high-dose irinotecan chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135(6):749–752. - PubMed
-
- Paduch R, Kandefer-Szerszen M, Piersiak T. The importance of release of proinflammatory cytokines, ROS, and NO in different stages of colon carcinoma growth and metastasis after treatment with cytotoxic drugs. Oncol Res. 2010;18(9):419–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

