Hemicraniectomy and durotomy upon deterioration from infarction-related swelling trial: randomized pilot clinical trial
- PMID: 24425122
- PMCID: PMC4033520
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003200
Hemicraniectomy and durotomy upon deterioration from infarction-related swelling trial: randomized pilot clinical trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Hemicraniectomy and Durotomy Upon Deterioration From Infarction-Related Swelling Trial (HeADDFIRST) was a randomized pilot study to obtain information necessary to design a Phase III trial to evaluate the benefit of surgical decompression for brain swelling from large supratentorial cerebral hemispheric infarction.
Methods: All patients with stroke were screened for eligibility (age 18-75 years, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale≥18 with Item 1a<2 [responsive to minor stimulation], and CT demonstrating unilateral, complete middle cerebral artery territory infarction by specific imaging criteria). All enrolled patients were treated using a standardized medical treatment protocol. Those with both≥4 mm of pineal shift and deterioration in level of arousal or ≥7.5 mm of anteroseptal shift within 96 hours of stroke onset were randomized to continued medical treatment only or medical treatment plus surgery. Death at 21 days was the primary outcome measure.
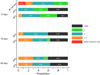
Results: Among 4909 screened patients, only 66 (1.3%) patients were eligible for HeADDFIRST. Forty patients were enrolled, and 26 patients developed the requisite brain swelling for randomization. All who failed to meet randomization criteria were alive at 21 days. Mortality at 21 and 180 days was 40% (4/10) in the medical treatment only and 21% (3/14) and 36% (5/14) in the medical treatment plus surgery arms, respectively.
Conclusions: HeADDFIRST randomization criteria effectively distinguished low from high risk of death from large supratentorial cerebral hemispheric infarction. Lower mortality in the medical treatment only group than in other published trials suggests a possible benefit to standardizing medical management. These results can inform the interpretation of recently completed European trials concerning patient selection and medical management.
Clinical trial registration: This trial was not registered because enrollment began before July 1, 2005.
Keywords: brain edema; craniectomy; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None
Figures


References
-
- Hacke W, Schwab S, Horn M, Spranger M, De Georgia M, von Kummer R. “Malignant” middle cerebral artery territory infarction: clinical course and prognostic signs. Arch Neurol. 1996;53:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Frank JI. Large hemispheric infarction, deterioration, and intracranial pressure. Neurology. 1995;45:1286–1290. - PubMed
-
- Hofmeijer J, Kappelle LJ, Algra A, Amelink GJ, van Gijn J, van der Worp HB. Surgical decompression for space-occupying cerebral infarction (the Hemicraniectomy After Middle Cerebral Artery infarction with Life-threatening Edema Trial [HAMLET]): a multicentre, open, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:326–333. - PubMed
-
- Jüttler E, Schwab S, Schmiedek P, Unterberg A, Hennerici M, Woitzik J, et al. Decompressive Surgery for the Treatment of Malignant Infarction of the Middle Cerebral Artery (DESTINY): a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke. 2007;38:2518–2525. - PubMed
-
- Vahedi K, Vicaut E, Mateo J, Kurtz A, Orabi M, Guichard J-P, et al. Sequential-design, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of early decompressive craniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (DECIMAL Trial) Stroke. 2007;38:2506–2517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

