Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 in adipocyte signaling
- PMID: 24425864
- PMCID: PMC3937697
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.506584
Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 in adipocyte signaling
Abstract
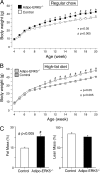
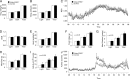
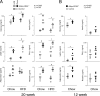
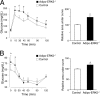
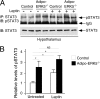
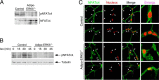
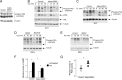
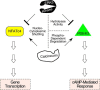
Increased adiposity due to energy imbalance is a critical factor of the epidemic crisis of obesity and type II diabetes. In addition to the obvious role in energy storage, regulatory factors are secreted from adipose depots to control appetite and cellular homeostasis. Complex signaling cross-talks within adipocyte are also evident due to the metabolic and immune nature of adipose depots. Here, we uncover a role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) in adipocyte signaling. We find that deletion of ERK5 in adipose depots (adipo-ERK5(-/-)) increases adiposity, in part, due to increased food intake. Dysregulated secretion of adipokines, leptin resistance, and impaired glucose handling are also found in adipo-ERK5(-/-) mice. Mechanistically, we show that ERK5 impinges on transcription factor NFATc4. Decreased phosphorylation at the conserved gate-keeping Ser residues and increased nuclear localization of NFATc4 are found in adipo-ERK5(-/-) mice. We also find attenuated PKA activation in adipo-ERK5(-/-) mice. In response to stimulation of β-adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor, we find decreased NFATc4 phosphorylation and impaired PKA activation in adipo-ERK5(-/-) mice. Reduced cAMP accumulation and increased phosphodiesterase activity are also found. Together, these results demonstrate integration of ERK5 with NFATc4 nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling and PKA activation in adipocyte signaling.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; MAP Kinases (MAPKs); Metabolic Regulation; NFAT Transcription Factor; Protein Kinase A (PKA).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integration of protein kinases mTOR and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 in regulating nucleocytoplasmic localization of NFATc4.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(10):3489-501. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01847-07. Epub 2008 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18347059 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of PKA and Rac signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 21;110(21):8531-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215902110. Epub 2013 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23657011 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid shear stress promotes osteoblast proliferation through the NFATc1-ERK5 pathway.Connect Tissue Res. 2019 Mar;60(2):107-116. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2018.1459588. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Connect Tissue Res. 2019. PMID: 29609502
-
Beyond Kinase Activity: ERK5 Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling as a Novel Target for Anticancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 31;21(3):938. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030938. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32023850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2.EMBO Rep. 2006 Aug;7(8):782-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400755. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16880823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ERK5 plays an essential role in gestational beta-cell proliferation.Cell Prolif. 2018 Jun;51(3):e12410. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12410. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 29159830 Free PMC article.
-
MEKK3-MEK5-ERK5 signaling promotes mitochondrial degradation.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Oct 20;6:107. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00342-7. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 33101709 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mir128-3p alleviates myocardial insulin resistance and prevents ischemia-induced heart failure.Elife. 2020 Mar 30;9:e54298. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54298. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32223896 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinases: mechanisms and downstream targets in inflammation-mediated obesity and insulin resistance.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Feb;426(1-2):27-45. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2878-8. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27868170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Conventional and Atypical MAPKs on the Development of Metabolic Diseases.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 29;10(9):1256. doi: 10.3390/biom10091256. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32872540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim S., Moustaid-Moussa N. (2000) Secretory, endocrine and autocrine/paracrine function of the adipocyte. J. Nutr. 130, 3110S–3115S - PubMed
-
- Steppan C. M., Lazar M. A. (2002) Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 18–23 - PubMed
-
- Rangwala S. M., Lazar M. A. (2000) Transcriptional control of adipogenesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 20, 535–559 - PubMed
-
- Rosen E. D., Walkey C. J., Puigserver P., Spiegelman B. M. (2000) Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 14, 1293–1307 - PubMed
-
- Collins S., Cao W., Robidoux J. (2004) Learning new tricks from old dogs. β-Adrenergic receptors teach new lessons on firing up adipose tissue metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 2123–2131 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

