Receptor-interacting protein 1 increases chemoresistance by maintaining inhibitor of apoptosis protein levels and reducing reactive oxygen species through a microRNA-146a-mediated catalase pathway
- PMID: 24425875
- PMCID: PMC3937640
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526152
Receptor-interacting protein 1 increases chemoresistance by maintaining inhibitor of apoptosis protein levels and reducing reactive oxygen species through a microRNA-146a-mediated catalase pathway
Abstract
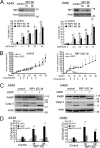
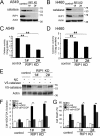
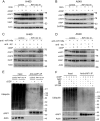
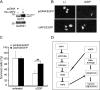
Although receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) is well known as a key mediator in cell survival and death signaling, whether RIP1 directly contributes to chemotherapy response in cancer has not been determined. In this report, we found that, in human lung cancer cells, knockdown of RIP1 substantially increased cytotoxicity induced by the frontline anticancer therapeutic drug cisplatin, which has been associated with robust cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and enhanced apoptosis. Scavenging ROS dramatically protected RIP1 knockdown cells against cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. Furthermore, we found that, in RIP1 knockdown cells, the expression of the hydrogen peroxide-reducing enzyme catalase was dramatically reduced, which was associated with increased miR-146a expression. Inhibition of microRNA-146a restored catalase expression, suppressed ROS induction, and protected against cytotoxicity in cisplatin-treated RIP1 knockdown cells, suggesting that RIP1 maintains catalase expression to restrain ROS levels in therapy response in cancer cells. Additionally, cisplatin significantly triggered the proteasomal degradation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 and 2 (c-IAP1 and c-IAP2), and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in a ROS-dependent manner, and in RIP1 knockdown cells, ectopic expression of c-IAP2 attenuated cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. Thus, our results establish a chemoresistant role for RIP1 that maintains inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) expression by release of microRNA-146a-mediated catalase suppression, where intervention within this pathway may be exploited for chemosensitization.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chemoresistance; Lung Cancer; RIP; Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retaining MKP1 expression and attenuating JNK-mediated apoptosis by RIP1 for cisplatin resistance through miR-940 inhibition.Oncotarget. 2014 Mar 15;5(5):1304-14. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1798. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24675421 Free PMC article.
-
RIP1 promotes proliferation through G2/M checkpoint progression and mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and necroptosis in human ovarian cancer cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Sep;41(9):1223-1233. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0340-7. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32242118 Free PMC article.
-
RIP1 potentiates BPDE-induced transformation in human bronchial epithelial cells through catalase-mediated suppression of excessive reactive oxygen species.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Sep;34(9):2119-28. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt143. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23633517 Free PMC article.
-
RIP1 post-translational modifications.Biochem J. 2022 May 13;479(9):929-951. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210725. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 35522161 Review.
-
The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in TNF-induced necrosis.Sci Signal. 2010 Mar 30;3(115):re4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3115re4. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20354226 Review.
Cited by
-
The Yin-Yang Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species and MicroRNAs in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 26;20(21):5335. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215335. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-491-5p negatively regulates cell proliferation and motility by targeting PDGFRA in prostate cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 1;7(12):2545-2553. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29312807 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H4 expression is cooperatively maintained by IKKβ and Akt1 which attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis through the DNA-PK/RIP1/IAPs signaling cascade.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 31;7:41715. doi: 10.1038/srep41715. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28139737 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2014 May 30;5(10):3333-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1948. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24830600 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of RIP1K and RIP3K expressions in the malignant and benign breast tumors.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):8849-56. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4762-7. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26749282
References
-
- Chang A. (2011) Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer 71, 3–10 - PubMed
-
- Maione P., Rossi A., Sacco P. C., Bareschino M. A., Schettino C., Gridelli C. (2010) Advances in chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 11, 2997–3007 - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R. A. (2011) Hallmarks of cancer. The next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

