Stress-induced ECM alteration modulates cellular microRNAs that feedback to readjust the extracellular environment and cell behavior
- PMID: 24427166
- PMCID: PMC3876577
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00305
Stress-induced ECM alteration modulates cellular microRNAs that feedback to readjust the extracellular environment and cell behavior
Abstract
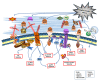
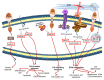
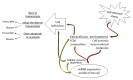
The extracellular environment is a complex entity comprising of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and regulatory molecules. It is highly dynamic and under cell-extrinsic stress, transmits the stressed organism's state to each individual ECM-connected cell. microRNAs (miRNAs) are regulatory molecules involved in virtually all the processes in the cell, especially under stress. In this review, we analyse how miRNA expression is regulated downstream of various signal transduction pathways induced by changes in the extracellular environment. In particular, we focus on the muscular dystrophy-associated cell adhesion molecule dystroglycan capable of signal transduction. Then we show how exactly the same miRNAs feedback to regulate the extracellular environment. The ultimate goal of this bi-directional signal transduction process is to change cell behavior under cell-extrinsic stress in order to respond to it accordingly.
Keywords: ECM composition; bi-directional signal transduction; dystroglycan; extrinsic stress; miRNAs.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

