Down syndrome's brain dynamics: analysis of fractality in resting state
- PMID: 24427209
- PMCID: PMC3713204
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-013-9248-y
Down syndrome's brain dynamics: analysis of fractality in resting state
Abstract
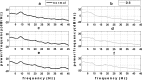
To the best knowledge of the authors there is no study on nonlinear brain dynamics of down syndrome (DS) patients, whereas brain is a highly complex and nonlinear system. In this study, fractal dimension of EEG, as a key characteristic of brain dynamics, showing irregularity and complexity of brain dynamics, was used for evaluation of the dynamical changes in the DS brain. The results showed higher fractality of the DS brain in almost all regions compared to the normal brain, which indicates less centrality and higher irregular or random functioning of the DS brain regions. Also, laterality analysis of the frontal lobe showed that the normal brain had a right frontal laterality of complexity whereas the DS brain had an inverse pattern (left frontal laterality). Furthermore, the high accuracy of 95.8 % obtained by enhanced probabilistic neural network classifier showed the potential of nonlinear dynamic analysis of the brain for diagnosis of DS patients. Moreover, the results showed that the higher EEG fractality in DS is associated with the higher fractality in the low frequencies (delta and theta), in broad regions of the brain, and the high frequencies (beta and gamma), majorly in the frontal regions.
Keywords: Down syndrome; EEG; Fractal dimension.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fractality analysis of frontal brain in major depressive disorder.Int J Psychophysiol. 2012 Aug;85(2):206-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 May 10. Int J Psychophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22580188
-
Fractality and a wavelet-chaos-neural network methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorder.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2010 Oct;27(5):328-33. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3181f40dc8. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20844443
-
Brain activity of women is more fractal than men.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Feb 22;535:7-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.12.043. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23313595
-
Nonlinear dynamical analysis of EEG and MEG: review of an emerging field.Clin Neurophysiol. 2005 Oct;116(10):2266-301. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2005.06.011. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16115797 Review.
-
Entropy and fractal analysis of brain-related neurophysiological signals in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.J Neural Eng. 2023 Sep 25;20(5). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acf8fa. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 37746822 Review.
Cited by
-
Everyday Memory in People with Down Syndrome.Brain Sci. 2021 Apr 27;11(5):551. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050551. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925503 Free PMC article.
-
Brain health in diverse settings: How age, demographics and cognition shape brain function.Neuroimage. 2024 Jul 15;295:120636. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120636. Epub 2024 May 21. Neuroimage. 2024. PMID: 38777219 Free PMC article.
-
Brain signal complexity in adults with Down syndrome: Potential application in the detection of mild cognitive impairment.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 20;14:988540. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.988540. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36337705 Free PMC article.
-
Computerized physical and cognitive training improves the functional architecture of the brain in adults with Down syndrome: A network science EEG study.Netw Neurosci. 2021 Mar 1;5(1):274-294. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00177. eCollection 2021. Netw Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33688615 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate multi-scale weighted permutation entropy analysis of EEG complexity for Alzheimer's disease.Cogn Neurodyn. 2017 Jun;11(3):217-231. doi: 10.1007/s11571-016-9418-9. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Cogn Neurodyn. 2017. PMID: 28559952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadlou M, Adeli H. Enhanced probabilistic neural network with local decision circles: a robust classifier. Integr Comput Aided Eng. 2010;17(3):197–210.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

