Endoscopic medial maxillectomy breaking new frontiers
- PMID: 24427611
- PMCID: PMC3718950
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-011-0393-5
Endoscopic medial maxillectomy breaking new frontiers
Abstract
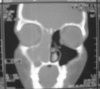
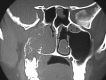
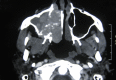
Endoscopy has changed the perspective of rhinologist towards the nose. It has revolutionised the surgical management of sinonasal disorders. Sinus surgeries were the first to get the benefit of endoscope. Gradually the domain of endoscopic surgery extended to the management of sino nasal tumours. Traditionally medial maxillectomy was performed through lateral rhinotomy or mid facial degloving approach. Endoscopic medial maxillectomy has been advocated by a number of authors in the management of benign sino-nasal tumours. We present our experience of endoscopic medial maxillectomy in the management of sinonasal pathologies.
Keywords: Endoscopic medial maxillectomy; Fungal sinusitis; Inverted papilloma.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Different endoscopic strategies in the management of recurrent sinonasal inverted papilloma.J Craniofac Surg. 2012 Jan;23(1):e44-8. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318241dae7. J Craniofac Surg. 2012. PMID: 22337461
-
Transnasal endoscopic medial maxillectomy for inverting papilloma.Laryngoscope. 2003 Apr;113(4):749-53. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200304000-00031. Laryngoscope. 2003. PMID: 12671441
-
Lateral rhinotomy vs mid-facial degloving for T3 inverted papilloma of nose and paranasal sinus.Nepal Med Coll J. 2009 Jun;11(2):115-7. Nepal Med Coll J. 2009. PMID: 19968152
-
Management of inverted papillomas of the nose and paranasal sinuses.Am J Otolaryngol. 2006 Jul-Aug;27(4):233-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2005.11.005. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 16798398 Review.
-
Management of sinonasal inverted papillomas: endoscopic medial maxillectomy.Med J Malaysia. 2008 Mar;63(1):58-60. Med J Malaysia. 2008. PMID: 18935736 Review.
References
-
- Keles N, Deger K. Endonasal endoscopic surgical treatment of paranasal sinus inverted papilloma: first experiences. Rhinology. 2001;39:156–157. - PubMed
-
- Sautter NB, Citardi MJ, Batra PS. Minimally invasive resection of frontal recess/sinus inverted papilloma. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2007;28:221–224. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
