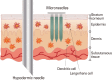
Microneedle patches for vaccine delivery
- PMID: 24427762
- PMCID: PMC3890449
- DOI: 10.7774/cevr.2014.3.1.42
Microneedle patches for vaccine delivery
Abstract
In today's medical industry, the range of vaccines that exist for administration in humans represents an eclectic variety of forms and immunologic mechanisms. Namely, these are the live attenuated viruses, inactivated viruses, subunit proteins, and virus-like particles for treating virus-caused diseases, as well as the bacterial-based polysaccharide, protein, and conjugated vaccines. Currently, a new approach to vaccination is being investigated with the concept of DNA vaccines. As an alternative delivery route to enhance the vaccination efficacy, microneedles have been devised to target the rich network of immunologic antigen-presenting cells in the dermis and epidermis layers under the skin. Numerous studies have outlined the parameters of microneedle delivery of a wide range of vaccines, revealing comparable or higher immunogenicity to conventional intramuscular routes, overall level of stability, and dose-sparing advantages. Furthermore, recent mechanism studies have begun to successfully elucidate the biological mechanisms behind microneedle vaccination. This paper describes the current status of microneedle vaccine research.
Keywords: Bacterial vaccines; DNA vaccines; Microneedles; Transdermal delivery; Virus vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Schwartz M. The life and works of Louis Pasteur. J Appl Microbiol. 2001;91:597–601. - PubMed
-
- Girard MP, Osmanov SK, Kieny MP. A review of vaccine research and development: the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Vaccine. 2006;24:4062–4081. - PubMed
-
- Dean CH, Alarcon JB, Waterston AM, et al. Cutaneous delivery of a live, attenuated chimeric flavivirus vaccine against Japanese encephalitis (ChimeriVax)-JE) in non-human primates. Hum Vaccin. 2005;1:106–111. - PubMed
-
- Hirschberg HJ, van de Wijdeven GG, Kraan H, Amorij JP, Kersten GF. Bioneedles as alternative delivery system for hepatitis B vaccine. J Control Release. 2010;147:211–217. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials