Lung cancer stigma, anxiety, depression, and quality of life
- PMID: 24428251
- PMCID: PMC4634635
- DOI: 10.1080/07347332.2013.855963
Lung cancer stigma, anxiety, depression, and quality of life
Abstract
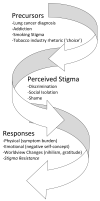
This study investigated lung cancer stigma, anxiety, depression, and quality of life (QOL) and validated variable similarities between ever and never smokers. Patients took online self-report surveys. Variable contributions to QOL were investigated using hierarchical multiple regression. Patients were primarily White females with smoking experience. Strong negative relationships emerged between QOL and anxiety, depression and lung cancer stigma. Lung cancer stigma provided significant explanation of the variance in QOL beyond covariates. No difference emerged between smoker groups for study variables. Stigma may play a role in predicting QOL. Interventions promoting social and psychological QOL may enhance stigma resistance skills.
References
-
- Arrieta O, Angulo LP, Nunez-Valencia C, Dorantes-Gallareta Y, Macedo EO, Martinez-Lopez D, Onate-Ocana LF. Association of Depression and Anxiety on Quality of Life, Treatment Adherence, and Prognosis in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2012 doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2793-5. - PubMed
-
- Balduyck B, Hendriks J, Sardari Nia P, Lauwers P, Van Schil P. Quality of life after lung cancer surgery: a review. [Review] Minerva Chirurgica. 2009;64(6):655–663. - PubMed
-
- Berger BE, Ferrans CE, Lashley FR. Measuring stigma in people with HIV: psychometric assessment of the HIV stigma scale. Evaluation Studies Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Research in Nursing & Health. 2001;24(6):518–529. - PubMed
-
- Buseh AG, Stevens PE. Constrained but not determined by stigma: Resistance by African American women living with HIV. Women & Health. 2006;44(3):1–18. doi: Doi 10.1300/J013v44n03_01. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical