Metformin induces PGC-1α expression and selectively affects hepatic PGC-1α functions
- PMID: 24428821
- PMCID: PMC3997275
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12585
Metformin induces PGC-1α expression and selectively affects hepatic PGC-1α functions
Abstract
Background and purpose: The objective of this study was to determine how the AMPK activating antidiabetic drug metformin affects the major activator of hepatic gluconeogenesis, PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and liver functions regulated by PGC-1α.
Experimental approach: Mouse and human primary hepatocytes and mice in vivo were treated with metformin. Adenoviral overexpression, siRNA and reporter gene constructs were used for mechanistic studies.
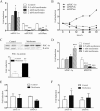
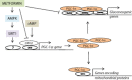
Key results: Metformin increased PGC-1α mRNA and protein expression in mouse primary hepatocytes. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) (another AMPK activator) had the opposite effect. Metformin also increased PGC-1α in human primary hepatocytes; this effect of metformin was abolished by AMPK inhibitor compound C and sirtuin 1 siRNA. AMPK overexpression by AMPK-Ad also increased PGC-1α. Whereas metformin increased PGC-1α, it down-regulated gluconeogenic genes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase). Furthermore, metformin attenuated the increase in PEPCK and G6Pase mRNAs induced by PGC-1α overexpression, but did not affect PGC-1α-mediated induction of mitochondrial genes. Metformin down-regulated several key transcription factors that mediate the effect of PGC-1α on gluconeogenic genes including Krüppel-like factor 15, forkhead box protein O1 and hepatocyte NF 4α, whereas it increased nuclear respiratory factor 1, which is involved in PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial proteins.
Conclusions and implications: Down-regulation of PGC-1α is not necessary for suppression of gluconeogenic genes by metformin. Importantly, metformin selectively affects hepatic PGC-1α-mediated gene regulation and prevents activation of gluconeogenesis, but does not influence its regulation of mitochondrial genes. These results identify selective modulation of hepatic PGC-1α functions as a novel mechanism involved in the therapeutic action of metformin.
Keywords: AMPK; G6Pase; PEPCK; PGC-1α; SIRT1; gluconeogenesis; liver; metformin.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Amat R, Planavila A, Chen SL, Iglesias R, Giralt M, Villarroya F. SIRT1 controls the transcription of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma co-activator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) gene in skeletal muscle through the PGC-1alpha autoregulatory loop and interaction with MyoD. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:21872–21880. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arpiainen S, Jarvenpaa SM, Manninen A, Viitala P, Lang MA, Pelkonen O, et al. Coactivator PGC-1alpha regulates the fasting inducible xenobiotic-metabolizing enzyme CYP2A5 in mouse primary hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008;232:135–141. - PubMed
-
- Caton PW, Nayuni NK, Kieswich J, Khan NQ, Yaqoob MM, Corder R. Metformin suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through induction of SIRT1 and GCN5. J Endocrinol. 2010;205:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

