Nephrologists' perspectives on dialysis treatment: results of an international survey
- PMID: 24428875
- PMCID: PMC3912927
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-16
Nephrologists' perspectives on dialysis treatment: results of an international survey
Abstract
Background: In-centre haemodialysis (ICHD) is the most common dialysis method used by patients worldwide. However, quality of life and clinical outcomes in patients treated via ICHD have not improved for some time. 'High-dose' haemodialysis (HD) regimens--which are longer and/or more frequent than conventional regimens and are particularly suitable to delivery in the home--may offer a route to improved outcomes and quality of life. This survey aimed to determine nephrologists' views on the validity of alternatives to ICHD, particularly home HD and high-dose HD.
Methods: A total of 1,500 nephrologists from Europe, Canada and the United States were asked to respond to an online questionnaire that was designed following previous qualitative research. Certified nephrologists in practice for 2-35 years who managed >25 adult dialysis patients were eligible to take part.
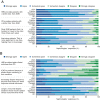
Results: A total of 324 nephrologists completed the survey. ICHD was the most common type of dialysis used by respondents' current patients (90%), followed by peritoneal dialysis (8%) and home HD (2%). The majority of respondents believed that: home HD provides better quality of life; increasing the frequency of dialysis beyond three times per week significantly improves clinical outcomes; and longer dialysis sessions performed nocturnally would result in significantly better clinical outcomes than traditional ICHD.
Conclusions: Survey results indicated that many nephrologists believe that home HD and high-dose HD are better for the patient. However, the majority of their patients were using ICHD. Education, training and support on alternative dialysis regimens are needed.
Figures

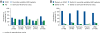
References
-
- U.S. Renal Data System. USRDS 2011: Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2011.
-
- ERA-EDTA Registry. ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2009. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Academic Medical Center, Department of Medical Informatics; 2011.
-
- Lameire N, van Biesen W, Vanholder R. Did 20 years of technological innovations in hemodialysis contribute to better patient outcomes? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(Suppl 1):S30–S40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

