Leukotriene B4 receptor 1 is differentially expressed on peripheral T cells of steroid-sensitive and -resistant asthmatics
- PMID: 24428972
- PMCID: PMC3951978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2013.12.006
Leukotriene B4 receptor 1 is differentially expressed on peripheral T cells of steroid-sensitive and -resistant asthmatics
Abstract
Background: Numbers of CD8(+) T cells expressing the leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptor, BLT1, have been correlated with asthma severity.
Objective: To examine the activation and numbers of BLT1-expressing peripheral blood CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells from patients with steroid-sensitive (SS) and steroid-resistant (SR) asthma.
Methods: CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells isolated from peripheral blood of healthy human subjects and patients with SS and SR asthma were stimulated in culture with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 followed by analysis of BLT1 surface expression and cytokine production. Activation of CD8(+) T cells after ligation of BLT1 by LTB4 was monitored by changes in intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations.
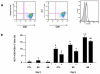
Results: The number of BLT1-expressing cells was larger in patients with asthma than in controls and larger on activated CD8(+) than on CD4(+) T cells. Addition of LTB4 to activated CD8(+) T cells resulted in increases in intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations. Expansion of activated CD4(+) T cells, unlike CD8(+) T cells, was significantly decreased in the presence of corticosteroid. In patients with SS asthma, numbers of BLT1-expressing CD8(+) T cells were lower in the presence of corticosteroid, unlike in those with SR asthma in whom cell expansion was maintained. Levels of interleukin-13 were highest in cultured CD8(+) T cells, whereas interleukin-10 levels were higher in CD4(+) T cells from controls and patients with SS asthma. Interferon-γ levels were lowest in patients with SR asthma.
Conclusion: Differences in BLT1 expression, steroid sensitivity, and cytokine production were demonstrated in T lymphocytes from patients with SS and SR asthma. The LTB4-BLT1 pathway in CD8(+) cells may play an important role in asthma and serve as an important target in the treatment of patients with SR asthma.
Copyright © 2014 American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
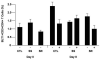

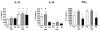
Similar articles
-
Importance of the leukotriene B4-BLT1 and LTB4-BLT2 pathways in asthma.Semin Immunol. 2017 Oct;33:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.005. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29042028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticosteroids enhance CD8+ T cell-mediated airway hyperresponsiveness and allergic inflammation by upregulating leukotriene B4 receptor 1.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Apr;121(4):864-71.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.01.035. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18395551
-
Requirement for leukotriene B4 receptor 1 in allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005 Jul 15;172(2):161-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200502-205OC. Epub 2005 Apr 22. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. PMID: 15849325 Free PMC article.
-
IL-13-producing BLT1-positive CD8 cells are increased in asthma and are associated with airway obstruction.Allergy. 2013;68(5):666-73. doi: 10.1111/all.12135. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23573812 Free PMC article.
-
The role of leukotriene B(4) in allergic diseases.Allergol Int. 2008 Dec;57(4):291-8. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.08-RAI-0019. Epub 2008 Dec 1. Allergol Int. 2008. PMID: 18797182 Review.
Cited by
-
Spectrum of T-lymphocyte activities regulating allergic lung inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2017 Jul;278(1):63-86. doi: 10.1111/imr.12561. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28658551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of T-Cell Immune Responses by Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 16;12:768133. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.768133. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of the leukotriene B4-BLT1 and LTB4-BLT2 pathways in asthma.Semin Immunol. 2017 Oct;33:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.005. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29042028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repetitive aeroallergen challenges elucidate maladaptive epithelial and inflammatory traits that underpin allergic airway diseases.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Aug;148(2):533-549. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.01.008. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33493557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CD8+ Tc2 cells: underappreciated contributors to severe asthma.Eur Respir Rev. 2019 Nov 20;28(154):190092. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0092-2019. Print 2019 Dec 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2019. PMID: 31748421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Larche M, Robinson DS, Kay AB. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:450–463. - PubMed
-
- Walker C, Bauer W, Braun RK, et al. Activated T cells and cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavages from patients with various lung diseases associated with eosinophilia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:1038–1048. - PubMed
-
- Lee SY, Kim SJ, Kwon SS, et al. Distribution and cytokine production of CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocyte subsets in patients with acute asthma attacks. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86:659–664. - PubMed
-
- Faul JL, Tormey VJ, Leonard C, et al. Lung immunopathology in cases of sudden asthma death. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:301–307. - PubMed
-
- van Rensen EL, Sont JK, Evertse CE, et al. Bronchial CD8 cell infiltrate and lung function decline in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:837–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

