Interneuron cell types are fit to function
- PMID: 24429630
- PMCID: PMC4349583
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12983
Interneuron cell types are fit to function
Abstract
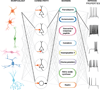
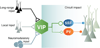
Understanding brain circuits begins with an appreciation of their component parts - the cells. Although GABAergic interneurons are a minority population within the brain, they are crucial for the control of inhibition. Determining the diversity of these interneurons has been a central goal of neurobiologists, but this amazing cell type has so far defied a generalized classification system. Interneuron complexity within the telencephalon could be simplified by viewing them as elaborations of a much more finite group of developmentally specified cardinal classes that become further specialized as they mature. Our perspective emphasizes that the ultimate goal is to dispense with classification criteria and directly define interneuron types by function.
Figures

References
-
-
Group PIN, et al. Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008;9:557–68. (Comment: the best effort to date by physiologists, anatomists and developmental neurobiologists to come to a common nomenclature for GABAergic interneurons).
-
-
- Freund TF, Buzsáki G. Interneurons of the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 1996;6:347–470. - PubMed
-
- Markram H, et al. Interneurons of the neocortical inhibitory system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004;5:793–807. - PubMed
-
- Parra P, Gulyás AI, Miles R. How Many Subtypes of Inhibitory Cells in the Hippocampus? Neuron. 1998;20:983–993. - PubMed
-
- Brody T, Odenwald WF. Regulation of temporal identities during Drosophila neuroblast lineage development. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2005;17:672–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

