A dose-ranging study of behavioral and pharmacological treatment in social settings for children with ADHD
- PMID: 24429997
- PMCID: PMC4090274
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-013-9843-8
A dose-ranging study of behavioral and pharmacological treatment in social settings for children with ADHD
Abstract
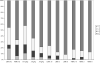
Placebo and three doses of methylphenidate (MPH) were crossed with 3 levels of behavioral modification (no behavioral modification, NBM; low-intensity behavioral modification, LBM; and high-intensity behavior modification, HBM) in the context of a summer treatment program (STP). Participants were 48 children with ADHD, aged 5-12. Behavior was examined in a variety of social settings (sports activities, art class, lunch) that are typical of elementary school, neighborhood, and after-school settings. Children received each behavioral condition for 3 weeks, order counterbalanced across groups. Children concurrently received in random order placebo, 0.15 mg/kg/dose, 0.3 mg/kg/dose, or 0.6 mg/kg/dose MPH, 3 times daily with dose manipulated on a daily basis in random order for each child. Both behavioral and medication treatments produced highly significant and positive effects on children's behavior. The treatment modalities also interacted significantly. Whereas there was a linear dose-response curve for medication in NBM, the dose-response curves flattened considerably in LBM and HBM. Behavior modification produced effects as large as moderate doses, and on some measures, high doses of medication. These results replicate and extend to social-recreational settings previously reported results in a classroom setting from the same sample (Fabiano et al., School Psychology Review, 36, 195-216, 2007). Results illustrate the importance of taking dosage/intensity into account when evaluating combined treatments; there were no benefits of combined treatments when the dosage of either treatment was high but combination of the low-dose treatments produced substantial incremental improvement over unimodal treatment.
Figures
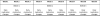



References
-
- Abikoff H, Hechtman L, Klein RG, Weiss G, Fleiss K, Etcovitch J, Pollack S. Symptomatic improvement in children with ADHD treated with long-term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2004;43:802–811. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000128791.10014.ac. - PubMed
-
- Abramowitz AJ, Eckstrand D, O'Leary SG, Dulcan MK. ADHD children's responses to stimulant medication and two intensities of a behavioral intervention. Behavior Modification. 1992;16:193–203. doi: 10.1177/01454455920162003. - PubMed
-
- Carlson CL, Pelham WE, Milich R, Dixon J. Single and combined effects of methylphenidate and behavior therapy on the classroom performance of children with ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 1992;20:213–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00916549. - PubMed
-
- Chronis AM, Fabiano GA, Gnagy EM, Onyango AN, Pelham WE, Williams A, Seymour K. An evaluation of the summer treatment program for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using a treatment withdrawal design. Behavior Therapy. 2004;35:561–585. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7894(04)80032-7.
-
- Chronis AM, Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Roberts JE, Aronoff HR. The impact of late-afternoon stimulant dosing for children with ADHD on parent and parent-child domains. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology. 2003;32:118–126. doi: 10.1207/S15374424JCCP3201_11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH062988/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012986/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA12986/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012414/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH092466/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD040935/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AA11873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R34 MH092466/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062946/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH065899/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA12414/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R34 MH078051/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH053554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH62988/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042080/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069614/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069434/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH065899/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD040935/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH62946/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH064243/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039087/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AA011873/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

