Hypothalamic inhibition of socio-sexual behaviour by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis
- PMID: 24430094
- PMCID: PMC3905723
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4061
Hypothalamic inhibition of socio-sexual behaviour by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis
Abstract
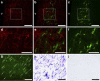
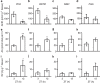
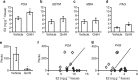
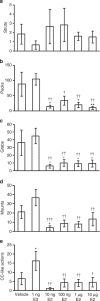
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide that inhibits gonadotropin secretion and socio-sexual behaviours. Oestrogen (neuroestrogen) synthesized in the brain from androgen by aromatase regulates male socio-sexual behaviours. Here we show that GnIH directly activates aromatase and increases neuroestrogen synthesis in the preoptic area (POA) and inhibits socio-sexual behaviours of male quail. Aromatase activity and neuroestrogen concentration in the POA are low in the morning when the birds are active, but neuroestrogen synthesis gradually increases until the evening when the birds become inactive. Centrally administered GnIH in the morning increases neuroestrogen synthesis in the POA and decreases socio-sexual behaviours. Centrally administered 17β-oestradiol at higher doses also inhibits socio-sexual behaviours in the morning. These results suggest that GnIH inhibits male socio-sexual behaviours by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis beyond its optimum concentration for the expression of socio-sexual behaviours. This is the first demonstration of any hypothalamic neuropeptide that directly regulates neuroestrogen synthesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone inhibits aggressive behavior of male quail by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis in the brain beyond its optimum concentration.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Sep 1;205:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.03.014. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24698787 Review.
-
Review: neuroestrogen regulation of socio-sexual behavior of males.Front Neurosci. 2014 Oct 13;8:323. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00323. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of testosterone and its metabolites on aromatase-immunoreactive cells in the quail brain: relationship with the activation of male reproductive behavior.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):185-200. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00236-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603040 Review.
-
Soya bean rich diet is associated with adult male rat aggressive behavior: relation to RF amide-related peptide 3-aromatase-neuroestrogen pathway in the brain.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Aug;34(4):1103-1115. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00431-2. Epub 2019 May 27. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 31134480
-
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone inhibits gonadal development and maintenance by decreasing gonadotropin synthesis and release in male quail.Endocrinology. 2006 Mar;147(3):1187-94. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1178. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16293662
Cited by
-
Structural and functional divergence of gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone from jawless fish to mammals.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Oct 24;5:177. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00177. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25386165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Female Japanese quail visually differentiate testosterone-dependent male attractiveness for mating preferences.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 3;8(1):10012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28368-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29968815 Free PMC article.
-
Food restriction-induced changes in motivation differ with stages of the estrous cycle and are closely linked to RFamide-related peptide-3 but not kisspeptin in Syrian hamsters.Physiol Behav. 2018 Jun 1;190:43-60. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Physiol Behav. 2018. PMID: 28624479 Free PMC article.
-
The Preoptic Area and the RFamide-Related Peptide Neuronal System Gate Seasonal Changes in Chemosensory Processing.Integr Comp Biol. 2017 Nov 1;57(5):1055-1065. doi: 10.1093/icb/icx099. Integr Comp Biol. 2017. PMID: 28985371 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen synthesized in the central nervous system enhances MC4R expression and reduces food intake.FEBS J. 2025 Aug;292(15):3900-3909. doi: 10.1111/febs.17426. Epub 2025 Feb 18. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 39967403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsutsui K. et al. A novel avian hypothalamic peptide inhibiting gonadotropin release. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 275, 661–667 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Ubuka T., Ukena K., Sharp P. J., Bentley G. E. & Tsutsui K. Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone inhibits gonadal development and maintenance by decreasing gonadotropin synthesis and release in male quail. Endocrinology 147, 1187–1194 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Tsutsui K. et al. Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) and its control of central and peripheral reproductive function. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 31, 284–295 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Ubuka T. & Bentley G. E. in: Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates, Birds Vol 4 eds Norris D. O., Lopez K. H. 1–25Academic Press (2010).
-
- Tsutsui K. & Ubuka T. Gonadotropin-inhibitory Hormone, in Handbook of biologically active peptides. Section on brain peptides eds Kastin A. J., Vaudry H. 802–811Academic Press (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

