Microsurgery in the urgent and emergent management of the hand
- PMID: 24431026
- PMCID: PMC4094114
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-013-9197-4
Microsurgery in the urgent and emergent management of the hand
Abstract
Appropriate use of microsurgical techniques in the emergency management of injured hands increases the salvage rate of complex upper limb injuries. Over time, the indications for replantation, both major and minor, have expanded and techniques refined to get better functional outcomes. The wide choice of free flaps available has made primary reconstruction possible to obtain a good functional and aesthetic outcome. The benefits microsurgery offers in the emergent management of the injured hand are now firmly established. The challenge is to create and maintain centers which can provide around-the-clock, high quality microsurgery services. The issues of adequate training opportunities, obtaining adequate work load to maintain high skill levels, attracting talent into the field are the challenges faced in maintaining high levels of service. In the developing countries, in addition to these issues, increasing the awareness of the potential of microsurgical services among the medical personal and the public has to be addressed.
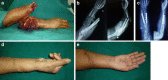
Figures
References
-
- Chen YC, Chan FC, Hsu CC, Lin YT, Chen CT, Lin CH. Fingertip replantation without venous anastomosis. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;70:284–288. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources