Human TH9 cells are skin-tropic and have autocrine and paracrine proinflammatory capacity
- PMID: 24431112
- PMCID: PMC4102325
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007828
Human TH9 cells are skin-tropic and have autocrine and paracrine proinflammatory capacity
Abstract
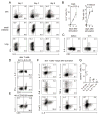
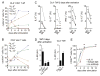
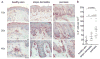
T helper type 9 (TH9) cells can mediate tumor immunity and participate in autoimmune and allergic inflammation in mice, but little is known about the TH9 cells that develop in vivo in humans. We isolated T cells from human blood and tissues and found that most memory TH9 cells were skin-tropic or skin-resident. Human TH9 cells coexpressed tumor necrosis factor-α and granzyme B and lacked coproduction of TH1/TH2/TH17 cytokines, and many were specific for Candida albicans. Interleukin-9 (IL-9) production was transient and preceded the up-regulation of other inflammatory cytokines. Blocking studies demonstrated that IL-9 was required for maximal production of interferon-γ, IL-9, IL-13, and IL-17 by skin-tropic T cells. IL-9-producing T cells were increased in the skin lesions of psoriasis, suggesting that these cells may contribute to human inflammatory skin disease. Our results indicate that human TH9 cells are a discrete T cell subset, many are tropic for the skin, and although they may function normally to protect against extracellular pathogens, aberrant activation of these cells may contribute to inflammatory diseases of the skin.
Conflict of interest statement
RAC and TSK previously had an equity interest in TremRX, a start-up company that seeks as a long-term business plan to improve vaccine formulation and delivery. During the period RAC and TSK held the equity, the interest was deemed to create a financial conflict of interest (as defined by the specific Public Health Serivce regulations) with the research discussed in this article. To resolve this matter, RAC and TSK divested themselves of the equity interest in this company, so this financial conflict of interest no longer exists. RAC has served as a consultant for Novartis, Dermira and Stiefel. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
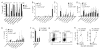


References
-
- Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos G, Gao W, Sobel RA, Mitsdoerffer M, Strom TB, Elyaman W, Ho IC, Khoury S, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9+ IL-10+ Foxp3(−) effector T cells. Nature immunology. 2008;9:1347–1355. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, Martin B, Wilhelm C, Stockinger B. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nature immunology. 2008;9:1341–1346. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm C, Turner JE, Van Snick J, Stockinger B. The many lives of IL-9: a question of survival? Nature immunology. 2012;13:637–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

