Investigation of synapse formation and function in a glutamatergic-GABAergic two-neuron microcircuit
- PMID: 24431444
- PMCID: PMC6608345
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0229-13.2014
Investigation of synapse formation and function in a glutamatergic-GABAergic two-neuron microcircuit
Abstract
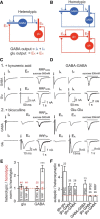
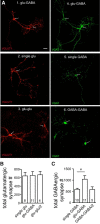
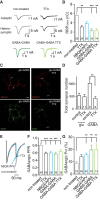
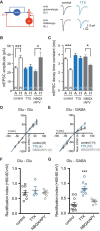
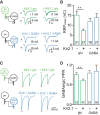
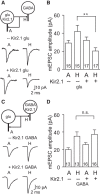
Neural circuits are composed of mainly glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons, which communicate through synaptic connections. Many factors instruct the formation and function of these synapses; however, it is difficult to dissect the contribution of intrinsic cell programs from that of extrinsic environmental effects in an intact network. Here, we perform paired recordings from two-neuron microculture preparations of mouse hippocampal glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons to investigate how synaptic input and output of these two principal cells develop. In our reduced preparation, we found that glutamatergic neurons showed no change in synaptic output or input regardless of partner neuron cell type or neuronal activity level. In contrast, we found that glutamatergic input caused the GABAergic neuron to modify its output by way of an increase in synapse formation and a decrease in synaptic release efficiency. These findings are consistent with aspects of GABAergic synapse maturation observed in many brain regions. In addition, changes in GABAergic output are cell wide and not target-cell specific. We also found that glutamatergic neuronal activity determined the AMPA receptor properties of synapses on the partner GABAergic neuron. All modifications of GABAergic input and output required activity of the glutamatergic neuron. Because our system has reduced extrinsic factors, the changes we saw in the GABAergic neuron due to glutamatergic input may reflect initiation of maturation programs that underlie the formation and function of in vivo neural circuits.
Keywords: GABAergic neuron; activity dependent; cell autonomous; cell culture; release probability; synapse formation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glutamatergic Innervation onto Striatal Neurons Potentiates GABAergic Synaptic Output.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 5;39(23):4448-4460. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2630-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30936241 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CX3CR1 Signaling on the Maturation of GABAergic Transmission and Neuronal Network Activity in the Neonate Hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2019 May 15;406:186-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30872165
-
Synaptic integration of newly generated neurons in rat dissociated hippocampal cultures.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jul;47(3):203-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 May 4. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21569851
-
Specific sets of intrinsic and extrinsic factors drive excitatory and inhibitory circuit formation.Neuroscientist. 2012 Jun;18(3):271-86. doi: 10.1177/1073858411404228. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Neuroscientist. 2012. PMID: 21652588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity-dependent development of GABAergic synapses.Brain Res. 2019 Mar 15;1707:18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30439352 Review.
Cited by
-
Shank1 regulates excitatory synaptic transmission in mouse hippocampal parvalbumin-expressing inhibitory interneurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Apr;41(8):1025-35. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12877. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25816842 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms governing Ca(2+) regulation of evoked and spontaneous release.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Jul;18(7):935-41. doi: 10.1038/nn.4044. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26108721 Review.
-
Altered Fast Synaptic Transmission in a Mouse Model of DNM1-Associated Developmental Epileptic Encephalopathy.eNeuro. 2021 Mar 10;8(2):ENEURO.0269-20.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0269-20.2020. Print 2021 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 33372033 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter expression level affects synaptic vesicle release probability at hippocampal synapses in culture.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 27;34(35):11781-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1444-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25164673 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding chronic pain: the glutamate-GABA tug of war in the cerebral cortex.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jul 23;18:1572775. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1572775. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40771361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chao HT, Chen H, Samaco RC, Xue M, Chahrour M, Yoo J, Neul JL, Gong S, Lu HC, Heintz N, Ekker M, Rubenstein JL, Noebels JL, Rosenmund C, Zoghbi HY. Dysfunction in GABA signalling mediates autism-like stereotypies and Rett syndrome phenotypes. Nature. 2010;468:263–269. doi: 10.1038/nature09582. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
