The emerging role of oxylipins in thrombosis and diabetes
- PMID: 24432004
- PMCID: PMC3882718
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00176
The emerging role of oxylipins in thrombosis and diabetes
Abstract
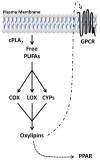
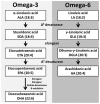
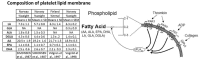
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD), the leading cause of death in the US, is predicted to increase due to the shift in age of the general population and increase in CVD risk factors such as obesity and diabetes. New therapies are required to decrease the prevalence of CVD risk factors (obesity and diabetes) as well as reduce atherothrombosis, the major cause of CVD related mortality. Oxylipins, bioactive metabolites derived from the oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, play a role in the progression of CVD risk factors and thrombosis. Aspirin, a cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor, decreases atherothrombotic associated mortality by 25%. These potent effects of aspirin have shown the utility of modulating oxylipin signaling pathways to decrease CVD mortality. The role of many oxylipins in the progression of CVD, however, is still uncertain or controversial. An increased understanding of the role oxylipins play in CVD risk factors and thrombosis could lead to new therapies to decrease the prevalence of CVD and its associated mortality.
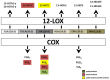
Keywords: 12-lipoxygenase, lipoxygenase; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; hemostasis; oxylipins; polyunsaturated fatty acids; thrombosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of oxylipins in cardiovascular diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Jul;39(7):1142-1154. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.24. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29877318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive lipid regulation of platelet function, hemostasis, and thrombosis.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Jun;246:108420. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108420. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37100208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of platelet function and thrombosis by omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018 Nov;139:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018. PMID: 30266534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Age, Menopause, and Obesity on Oxylipins Linked to Vascular Health.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Feb;41(2):883-897. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315133. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33380172
-
Advances in Our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs.Adv Nutr. 2015 Sep 15;6(5):513-40. doi: 10.3945/an.114.007732. Print 2015 Sep. Adv Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26374175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photoperiod Conditions Modulate Serum Oxylipins Levels in Healthy and Obese Rats: Impact of Proanthocyanidins and Gut Microbiota.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 30;15(3):707. doi: 10.3390/nu15030707. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36771413 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl Sulfoxide Decreases Levels of Oxylipin Diols in Mouse Liver.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 29;10:580. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00580. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31191316 Free PMC article.
-
Ability of a Polyphenol-Rich Nutraceutical to Reduce Central Nervous System Lipid Peroxidation by Analysis of Oxylipins in Urine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;12(3):721. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030721. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978969 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of Lipid Homeostasis: A Fa(c)t in the Development of Metabolic Diseases.Cells. 2020 Dec 4;9(12):2605. doi: 10.3390/cells9122605. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33291746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Role of Phospholipases A2 in Health and Diseases in the Central Nervous System.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2963. doi: 10.3390/cells10112963. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler D. H., Cogan J. D., Phillips J. A., III, Schnetz-Boutaud N., Milne G. L., Iverson T., et al. (2008). Inherited human cPLA(2alpha) deficiency is associated with impaired eicosanoid biosynthesis, small intestinal ulceration, and platelet dysfunction. J. Clin. Invest. 118 2121–2131 10.1172/JCI30473 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

