Anti-CD20 as the B-Cell Targeting Agent in a Combined Therapy to Modulate Anti-Factor VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia a Inhibitor Mice
- PMID: 24432019
- PMCID: PMC3881000
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00502
Anti-CD20 as the B-Cell Targeting Agent in a Combined Therapy to Modulate Anti-Factor VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia a Inhibitor Mice
Abstract
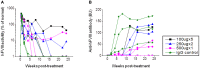
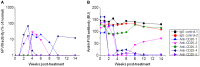
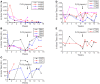
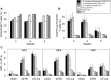
Neutralizing antibody formation against transgene products can represent a major complication following gene therapy with treatment of genetic diseases, such as hemophilia A. Although successful approaches have been developed to prevent the formation of anti-factor VIII (FVIII) antibodies, innovative strategies to overcome pre-existing anti-FVIII immune responses in FVIII-primed subjects are still lacking. Anti-FVIII neutralizing antibodies circulate for long periods in part due to persistence of memory B-cells. Anti-CD20 targets a variety of B-cells (pre-B-cells to mature/memory cells); therefore, we investigated the impact of B-cell depletion on anti-FVIII immune responses in hemophilia A mice using anti-CD20 combined with regulatory T (Treg) cell expansion using IL-2/IL-2mAb complexes plus rapamycin. We found that anti-CD20 alone can partially modulate anti-FVIII immune responses in both unprimed and FVIII-primed hemophilia A mice. Moreover, in mice treated with anti-CD20+IL-2/IL-2mAb complexes+rapamycin+FVIII, anti-FVIII antibody titers were significantly reduced in comparison to mice treated with regimens targeting only B or T cells. In addition, titers remained low after a second challenge with FVIII plasmid. Treg cells and activation markers were transiently and significantly increased in the groups treated with IL-2/IL-2mAb complexes; however, significant B-cell depletion was obtained in anti-CD20-treated groups. Importantly, both FVIII-specific antibody-secreting cells and memory B-cells were significantly reduced in mice treated with combination therapy. This study demonstrates that a combination regimen is highly promising as a treatment option for modulating anti-FVIII antibodies and facilitating induction of long-term tolerance to FVIII in hemophilia A mice.
Keywords: B-cell depletion; anti-CD20; factor VIII; hemophilia; immunomodulation; tolerance induction.
Figures

References
-
- Darby SC, Keeling DM, Spooner RJ, Wan Kan S, Giangrande PL, Collins PW, et al. The incidence of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in the hemophilia population of the UK and their effect on subsequent mortality, 1977–99. J Thromb Haemost (2004) 2(7):1047–5410.1046/j.1538-7836.2004.00710.x - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

