Hip surveillance and management of the displaced hip in cerebral palsy
- PMID: 24432103
- PMCID: PMC3838516
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-013-0515-6
Hip surveillance and management of the displaced hip in cerebral palsy
Abstract
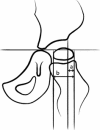
Introduction: This article provides an overview of the management of a displaced hip in children with cerebral palsy and considers surveillance programmes, principles of surgical reconstruction and options for the salvage of an unreconstructable hip in these children.
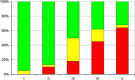
Conclusion: Hip dislocation in CP is potentially preventable if children are included from an early age in a surveillance programme that includes repeat radiographic and clinical examinations, and preventive treatment for hips that are displacing. A surveillance programme should be based on the child's age, GMFCS level and migration percentage (MP), and surgical prevention may be considered in children with a MP exceeding 33 %.
Keywords: Cerebral palsy; Child; Hip displacement; Operative management; Surveillance programme.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characteristics of children with hip displacement in cerebral palsy.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007 Oct 26;8:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-8-101. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007. PMID: 17963501 Free PMC article.
-
The head shaft angle is associated with hip displacement in children at GMFCS levels III-V - a population based study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Oct 5;19(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s12891-018-2275-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 30286753 Free PMC article.
-
Hip displacement in children with cerebral palsy.Bone Joint J. 2021 Feb;103-B(2):411-414. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B2.BJJ-2020-1528.R1. Bone Joint J. 2021. PMID: 33517734
-
The effectiveness of European Hip Surveillance Programmes in the identification and management of hip displacement and hip dislocation in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review.Disabil Rehabil. 2025 May 31:1-10. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2025.2512407. Online ahead of print. Disabil Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40450389 Review.
-
Hip Displacement in Cerebral Palsy: The Role of Surveillance.Indian J Orthop. 2020 Jun 11;55(1):5-19. doi: 10.1007/s43465-020-00162-y. eCollection 2021 Feb. Indian J Orthop. 2020. PMID: 33569095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Principles of treatment of spastic palsy in children: a critical review].Orthopade. 2014 Jul;43(7):643-8. doi: 10.1007/s00132-013-2218-6. Orthopade. 2014. PMID: 24939715 Review. German.
-
An automated framework for pediatric hip surveillance and severity assessment using radiographs.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025 Jan;20(1):203-211. doi: 10.1007/s11548-024-03254-4. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025. PMID: 39283409
-
Pelvis radiographs in children with cerebral palsy: effects of patient positioning on calculating migration percentages.Pediatr Radiol. 2023 Dec;53(13):2662-2671. doi: 10.1007/s00247-023-05783-7. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Pediatr Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37833504
-
Development of a standards-based phenotype model for gross motor function to support learning health systems in pediatric rehabilitation.Learn Health Syst. 2021 May 5;6(1):e10266. doi: 10.1002/lrh2.10266. eCollection 2022 Jan. Learn Health Syst. 2021. PMID: 35036550 Free PMC article.
-
From Hip Screening to Hip Surveillance: Transforming Care for Patients With Cerebral Palsy: An Analysis of a Single Institution.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023 Dec 8;7(12):e23.00236. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00236. eCollection 2023 Dec 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 38063442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tachdjian MO, Minear WL (1956) Hip dislocation in cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 38A:1358–1364 - PubMed
-
- Miller F (2005) In: Cerebral palsy. Springer, Berlin, pp 524–525
-
- Brown JK, Minns RA. Mechanisms of deformity in children with cerebral palsy. Sem Orthop. 1989;4:236–255.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

