A disseminated infection with the antifungal-multiresistant teleomorphic fungus Neocosmospora vasinfecta in a patient with acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 24432214
- PMCID: PMC3885941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2013.01.004
A disseminated infection with the antifungal-multiresistant teleomorphic fungus Neocosmospora vasinfecta in a patient with acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
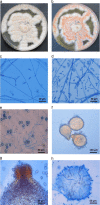
We report on a fatal invasive infection due to the ascomycetous fungus Neocosmospora vasinfecta, in a 20-year-old European patient suffering from an acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The infection could not be controlled by a bitherapy combining liposomal amphotericin B and voriconazole. This is the second case of disseminated infection reported with this unusual fungus, which develops under its teleomorphic state, is fully resistant to all systemic antifungals, and which is known to live in tropical countries.
Keywords: Antifungal-resistance; Invasive fungal infection; Neocosmospora vasinfecta; Teleomorph.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disseminated Neocosmospora vasinfecta infection in a patient with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.Emerg Infect Dis. 2001 Jan-Feb;7(1):149-52. doi: 10.3201/eid0701.700149. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11266308 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of Soybean Neocosmospora Stem Rot Caused by Neocosmospora vasinfecta var. vasinfecta in China.Plant Dis. 2011 Aug;95(8):1031. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-11-0287. Plant Dis. 2011. PMID: 30732095
-
Corneal ulcer due to Neocosmospora vasinfecta in an immunocompetent patient.Med Mycol. 2008 May;46(3):279-84. doi: 10.1080/13693780701625149. Med Mycol. 2008. PMID: 17885942
-
Liposomal amphotericin B: a review of its use as empirical therapy in febrile neutropenia and in the treatment of invasive fungal infections.Drugs. 2009;69(3):361-92. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00010. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19275278 Review.
-
Isolated pulmonary fusariosis caused by Neocosmospora pseudensiformis in a liver transplant recipient: A case report and review of the literature.Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;22(6):e13344. doi: 10.1111/tid.13344. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32479709 Review.
Cited by
-
Species Diversity in the Fusarium solani (Neocosmospora) Complex and Their Pathogenicity for Plants and Humans.Dokl Biol Sci. 2022 Dec;507(1):416-427. doi: 10.1134/S0012496622060217. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Dokl Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36781537
-
Comparative Genomics and Transcriptomics During Sexual Development Gives Insight Into the Life History of the Cosmopolitan Fungus Fusarium neocosmosporiellum.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 7;10:1247. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01247. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31231336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kac G., Piriou P., Gueho E., Roux P., Tremoulet J., Denis M. Osteoarthritis caused by Neocosmospora vasinfecta. Medical Mycology. 1999;37:213–217. - PubMed
-
- Manikandan P., Vágvölgyi C., Narendran V., Panneer Selvam K., Kredics L. Neocosmosporas. In: Liu D., editor. Molecular detection of human fungal pathogens. CRC Press; 2011. p. 449–58.
-
- Chandenier J., Hayette M.P., De Bièvre C., Westeel P.F., Petit J., Achard J.M. Tuméfaction de la jambe à Neocosmospora vasinfecta chez un transplanté rénal - Premier cas d’infection humaine. Journal de Mycologie Médicale. 1993;3:165–168.
-
- Manikandan P., Vismer H.F., Kredics L., Dóczi I., Marasas W.F.O., Bhaskar M. Corneal ulcer due to Neocosmospora vasinfecta in an immunocompetent patient. Medical Mycology. 2007;46:279–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

