Body mass index categories and mortality risk in US adults: the effect of overweight and obesity on advancing death
- PMID: 24432921
- PMCID: PMC3953803
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301597
Body mass index categories and mortality risk in US adults: the effect of overweight and obesity on advancing death
Abstract
Objectives: We examined the association of body mass index with all-cause and cardiovascular disease (CVD)-specific mortality risks among US adults and calculated the rate advancement period by which death is advanced among the exposed groups.
Methods: We used data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988-1994) linked to the National Death Index mortality file with follow-up to 2006 (n = 16 868). We used Cox proportional hazards regression to estimate the rate of dying and rate advancement period for all-cause and CVD-specific mortality for overweight and obese adults relative to their normal-weight counterparts.
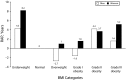
Results: Compared with normal-weight adults, obese adults had at least 20% significantly higher rate of dying of all-cause or CVD. These rates advanced death by 3.7 years (grades II and III obesity) for all-cause mortality and between 1.6 (grade I obesity) and 5.0 years (grade III obesity) for CVD-specific mortality. The burden of obesity was greatest among adults aged 45 to 64 years for all-cause and CVD-specific mortality and among women for all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the impact of the obesity epidemic on mortality risk and premature deaths among US adults.
Figures

References
-
- Health, United States, 2010: With Special Feature on Death and Dying. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CL. Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22(1):39–47. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295(13):1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- McGinnis JM, Foege WH. Actual causes of death in the United States. JAMA. 1993;270(18):2207–2212. - PubMed
-
- Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, VanItallie TB. Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA. 1999;282(16):1530–1538. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

