Plasma protein profiling of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's disease using iTRAQ quantitative proteomics
- PMID: 24433274
- PMCID: PMC3898732
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-12-5
Plasma protein profiling of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's disease using iTRAQ quantitative proteomics
Abstract
Background: With the promise of disease modifying treatments, there is a need for more specific diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Plasma biomarkers are likely to be utilised to increase diagnostic accuracy and specificity of AD and cognitive decline.
Methods: Isobaric tags (iTRAQ) and proteomic methods were used to identify potential plasma biomarkers of MCI and AD. Relative protein expression level changes were quantified in plasma of 411 cognitively normal subjects, 19 AD patients and 261 MCI patients. Plasma was pooled into 4 groups including normal control, AD, amnestic single and multiple domain MCI (aMCI), and nonamnestic single and multiple domain MCI (nMCI). Western-blotting was used to validate iTRAQ data. Integrated function and protein interactions were explored using WEB based bioinformatics tools (DAVID v6.7 and STRING v9.0).
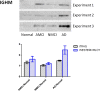
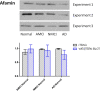
Results: In at least two iTRAQ replicate experiments, 30 proteins were significantly dysregulated in MCI and AD plasma, relative to controls. These proteins included ApoA1, ApoB100, complement C3, C4b-binding protein, afamin, vitamin D-binding protein precursor, isoform 1 of Gelsolin actin regulator, Ig mμ chain C region (IGHM), histidine-rich glycoprotein and fibrinogen β and γ chains. Western-blotting confirmed that afamin was decreased and IGHM was increased in MCI and AD groups. Bioinformatics results indicated that these dysregulated proteins represented a diversity of biological processes, including acute inflammatory response, cholesterol transport and blood coagulation.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that expression level changes in multiple proteins are observed in MCI and AD plasma. Some of these, such as afamin and IGHM, may be candidate biomarkers for AD and the predementia condition of MCI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma protein profiling of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease across two independent cohorts.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43(4):1355-73. doi: 10.3233/JAD-141266. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25159666
-
Plasma protein profiling for potential biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Neurol Res. 2017 Mar;39(3):231-238. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2017.1281195. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Neurol Res. 2017. PMID: 28107809
-
Increased Plasma Beta-Secretase 1 May Predict Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease Dementia in Individuals With Mild Cognitive Impairment.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Mar 1;83(5):447-455. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28359566 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Rev. 2009 Oct;61(2):69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 21. Brain Res Rev. 2009. PMID: 19464319 Review.
-
Core candidate neurochemical and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2008 Jan;4(1):38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2007.08.006. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2008. PMID: 18631949 Review.
Cited by
-
Why Inclusion Matters for Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Discovery in Plasma.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;79(3):1327-1344. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201318. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33427747 Free PMC article.
-
The association of depression, cognitive impairment without dementia, and dementia with risk of ischemic stroke: a cohort study.Psychosom Med. 2015 Feb-Mar;77(2):200-8. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000136. Psychosom Med. 2015. PMID: 25647752 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using Quantitative Mass Spectrometry of Human Blood Plasma Proteins and Machine Learning.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 18;23(14):7907. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147907. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887259 Free PMC article.
-
Which neuroimaging and fluid biomarkers method is better in theranostic of Alzheimer's disease? An umbrella review.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;16:403-417. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.02.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38497046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iTRAQ-based Proteomic Analysis of APPSw,Ind Mice Provides Insights into the Early Changes in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(10):1109-1122. doi: 10.2174/1567205014666170719165745. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017. PMID: 28730955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cutler P, Akuffo E, Briggs D, Bodnar W, Debouck C, Fox S, Bibson R, Gormley D, Holbrook J, Hunter A. et al.Proteomic identification and early validation of complement 1 inhibitor and pigment epithelium-derived factor: two novel biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease in human plasma. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2008;2:467–477. doi: 10.1002/prca.200780101. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous