Morphological changes of cortical pyramidal neurons in hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 24433342
- PMCID: PMC3898242
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-15
Morphological changes of cortical pyramidal neurons in hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a reversible neuropsychiatric syndrome associated with acute and chronic liver diseases. It includes a number of neuropsychiatric disturbances including impaired motor activity and coordination, intellectual and cognitive function.
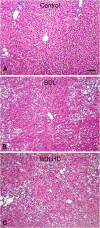
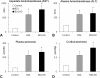
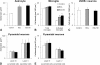
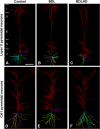
Results: In the present study, we used a chronic rat HE model by ligation of the bile duct (BDL) for 4 weeks. These rats showed increased plasma ammonia level, bile duct hyperplasia and impaired spatial learning memory and motor coordination when tested with Rota-rod and Morris water maze tests, respectively. By immunohistochemistry, the cerebral cortex showed swelling of astrocytes and microglia activation. To gain a better understanding of the effect of HE on the brain, the dendritic arbors of layer V cortical pyramidal neurons and hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons were revealed by an intracellular dye injection combined with a 3-dimensional reconstruction. Although the dendritic arbors remained unaltered, the dendritic spine density on these neurons was significantly reduced. It was suggested that the reduction of dendritic spines may be the underlying cause for increased motor evoked potential threshold and prolonged central motor conduction time in clinical finding in cirrhosis.
Conclusions: We found that HE perturbs CNS functions by altering the dendritic morphology of cortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons, which may be the underlying cause for the motor and intellectual impairments associated with HE patients.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

