The M50I polymorphic substitution in association with the R263K mutation in HIV-1 subtype B integrase increases drug resistance but does not restore viral replicative fitness
- PMID: 24433497
- PMCID: PMC3898230
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-11-7
The M50I polymorphic substitution in association with the R263K mutation in HIV-1 subtype B integrase increases drug resistance but does not restore viral replicative fitness
Abstract
Background: First-generation integrase strand-transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), such as raltegravir (RAL) and elvitegravir (EVG), have been clinically proven to be effective antiretrovirals for the treatment of HIV-positive patients. However, their relatively low genetic barrier for resistance makes them susceptible to the emergence of drug resistance mutations. In contrast, dolutegravir (DTG) is a newer INSTI that appears to have a high genetic barrier to resistance in vivo. However, the emergence of the resistance mutation R263K followed by the polymorphic substitution M50I has been observed in cell culture. The M50I polymorphism is also observed in 10-25% of INSTI-naïve patients and has been reported in combination with R263K in a patient failing treatment with RAL.
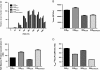
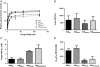
Results: Using biochemical cell-free strand-transfer assays and resistance assays in TZM-bl cells, we demonstrate that the M50I polymorphism in combination with R263K increases resistance to DTG in tissue culture and in biochemical assays but does not restore the viral fitness cost associated with the R263K mutation.
Conclusions: Since the combination of the R263K mutation and the M50I polymorphism results in a virus with decreased viral fitness and limited cross-resistance, the R263K resistance pathway may represent an evolutionary dead-end. Although this hypothesis has not yet been proven, it may be more advantageous to treat HIV-positive individuals with DTG in first-line than in second or third-line therapy.
Figures
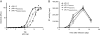
References
-
- Hightower KE, Wang R, DeAnda F, Johns BA, Weaver K, Shen Y, Tomberlin GH, Carter HL, Broderick T, Sigethy S. Dolutegravir (S/GSK1349572) exhibits significantly slower dissociation than raltegravir and elvitegravir from wild-type and integrase inhibitor-resistant HIV-1 integrase-DNA complexes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:4552–4559. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00157-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wainberg MA, Mesplède T, Quashie PK. The development of novel HIV integrase inhibitors and the problem of drug resistance. Current Opinion in Virology. 2012;2656:662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

