Distribution and morphology of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P immunoreactive axons in the whole-mount atria of mice
- PMID: 24433968
- PMCID: PMC10506417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2013.12.010
Distribution and morphology of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P immunoreactive axons in the whole-mount atria of mice
Abstract
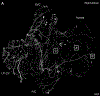
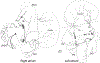
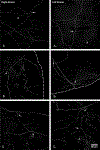
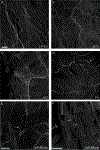
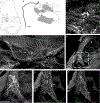
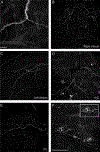
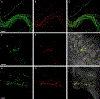
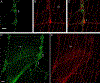
The murine model has been used to investigate the role of cardiac sensory axons in various disease states. However, the distribution and morphological structures of cardiac nociceptive axons in normal murine tissues have not yet been well characterized. In this study, whole-mount atria from FVB mice were processed with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) primary antibodies followed by secondary antibodies, and then examined using confocal microscopy. We found: 1) Large CGRP-IR axon bundles entered the atria with the major veins, and these large bundles bifurcated into small bundles and single axons that formed terminal end-nets and free endings in the epicardium. Varicose CGRP-IR axons had close contacts with muscle fibers, and some CGRP-IR axons formed varicosities around principle neurons (PNs) within intrinsic cardiac ganglia (ICGs). 2) SP-IR axons also were found in the same regions of the atria, attached to veins, and within cardiac ganglia. Similar to CGRP-IR axons, these SP-IR axons formed terminal end-nets and free endings in the atrial epicardium and myocardium. Within ICGs, SP-IR axons formed varicose endings around PNs. However, SP-IR nerve fibers were less abundant than CGRP-IR fibers in the atria. 3) None of the PNs were CGRP-IR or SP-IR. 4) CGRP-IR and SP-IR often colocalized in terminal varicosities around PNs. Collectively, our data document the distribution pattern and morphology of CGRP-IR and SP-IR axons and terminals in different regions of the atria. This knowledge provides useful information for CGRP-IR and SP-IR axons that can be referred to in future studies of pathological remodeling.
Keywords: Atria; CGRP; Cardiac ganglia; Neuropeptides; Nociceptive; SP.
Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Organization and morphology of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive axons in the whole mouse stomach.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Nov;531(16):1608-1632. doi: 10.1002/cne.25519. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37694767 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and morphology of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) innervation in flat mounts of whole rat atria and ventricles.Auton Neurosci. 2024 Feb;251:103127. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2023.103127. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Auton Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38211380 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-immunoreactive axons in the nucleus gracilis of the rat with special reference to axonal dystrophy: light and electron microscopic observations.Acta Neuropathol. 1995;90(4):347-55. doi: 10.1007/BF00315008. Acta Neuropathol. 1995. PMID: 8546025
-
From sensation to regulation: the diverse functions of peripheral sensory nervous system.Front Immunol. 2025 May 16;16:1575917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575917. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40453085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulation of Pulmonary Vascular Tone by Neuropeptides and the Implications for Pulmonary Hypertension.Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 23;9:1167. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01167. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30190678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurochemical alterations of intrinsic cardiac ganglionated nerve plexus caused by arterial hypertension developed during ageing in spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar Kyoto rats.J Anat. 2023 Oct;243(4):630-647. doi: 10.1111/joa.13877. Epub 2023 Apr 21. J Anat. 2023. PMID: 37083051 Free PMC article.
-
Organization and morphology of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive axons in the whole mouse stomach.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Nov;531(16):1608-1632. doi: 10.1002/cne.25519. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37694767 Free PMC article.
-
3D single cell scale anatomical map of sex-dependent variability of the rat intrinsic cardiac nervous system.iScience. 2021 Jul 19;24(7):102795. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102795. eCollection 2021 Jul 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34355144 Free PMC article.
-
Topographical mapping of catecholaminergic axon innervation in the flat-mounts of the mouse atria: a quantitative analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 7;13(1):4850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27727-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37029119 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia remodels catecholaminergic nerve innervation in mouse atria.J Physiol. 2024 Jan;602(1):49-71. doi: 10.1113/JP284961. Epub 2023 Dec 29. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38156943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai J, Epstein PN, Gozal D, Yang B, Wurster RD, Cheng ZJ, 2007a. Morphology and topography of nucleus ambiguus projections to cardiac ganglia in rats and mice. Neuroscience 149, 845–860. - PubMed
-
- Ai J, Gozal D, Li L, Wead WB, Chapleau MW, Wurster RD, Yang B, Li H, Liu R, Cheng Z, 2007b. Degeneration of vagal efferent axons and terminals in cardiac ganglia of aged rats. J. Comp. Neurol 504, 74–88. - PubMed
-
- Ai J, Wurster RD, Harden SW, Cheng ZJ, 2009. Vagal afferent innervation and remodeling in the aortic arch of young-adult Fischer 344 rats following chronic intermittent hypoxia. Neuroscience 164, 658–666. - PubMed
-
- Becker DE, Ancin H, Szarowski DH, Turner JN, Roysam B, 1996. Automated 3-D montage synthesis from laser-scanning confocal images: application to quantitative tissue-level cytological analysis. Cytometry 25, 235–245. - PubMed
-
- Benemei S, Nicoletti P, Capone JG, Geppetti P, 2009. CGRP receptors in the control of pain and inflammation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol 9, 9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

