Prolactin and teleost ionocytes: new insights into cellular and molecular targets of prolactin in vertebrate epithelia
- PMID: 24434597
- PMCID: PMC4096611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.12.014
Prolactin and teleost ionocytes: new insights into cellular and molecular targets of prolactin in vertebrate epithelia
Abstract
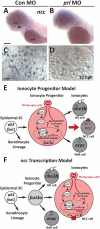
The peptide hormone prolactin is a functionally versatile hormone produced by the vertebrate pituitary. Comparative studies over the last six decades have revealed that a conserved function for prolactin across vertebrates is the regulation of ion and water transport in a variety of tissues including those responsible for whole-organism ion homeostasis. In teleost fishes, prolactin was identified as the "freshwater-adapting hormone", promoting ion-conserving and water-secreting processes by acting on the gill, kidney, gut and urinary bladder. In mammals, prolactin is known to regulate renal, intestinal, mammary and amniotic epithelia, with dysfunction linked to hypogonadism, infertility, and metabolic disorders. Until recently, our understanding of the cellular mechanisms of prolactin action in fishes has been hampered by a paucity of molecular tools to define and study ionocytes, specialized cells that control active ion transport across branchial and epidermal epithelia. Here we review work in teleost models indicating that prolactin regulates ion balance through action on ion transporters, tight-junction proteins, and water channels in ionocytes, and discuss recent advances in our understanding of ionocyte function in the genetically and embryonically accessible zebrafish (Danio rerio). Given the high degree of evolutionary conservation in endocrine and osmoregulatory systems, these studies in teleost models are contributing novel mechanistic insight into how prolactin participates in the development, function, and dysfunction of osmoregulatory systems across the vertebrate lineage.
Keywords: Differentiation; Gill; NCC; Osmoregulation; Pituitary; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endocrine control of gill ionocyte function in euryhaline fishes.J Comp Physiol B. 2024 Oct;194(5):663-684. doi: 10.1007/s00360-024-01555-3. Epub 2024 May 13. J Comp Physiol B. 2024. PMID: 38739280 Review.
-
Prolactin and cortisol mediate the maintenance of hyperosmoregulatory ionocytes in gills of Mozambique tilapia: Exploring with an improved gill incubation system.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2016 Jun 1;232:151-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.04.024. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27118703
-
Ontogeny of osmoregulation in postembryonic fish: a review.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2005 Aug;141(4):401-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2005.01.013. Epub 2005 Feb 25. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16140237 Review.
-
New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2012 Dec 1;184(3):257-68. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2012.07.019. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22850177 Review.
-
Prolactin regulates transcription of the ion uptake Na+/Cl- cotransporter (ncc) gene in zebrafish gill.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Apr 30;369(1-2):98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.01.021. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23395804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of transfer from steady-state to tidally-changing salinities on plasma and branchial osmoregulatory variables in adult Mozambique tilapia.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019 Jan;227:134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30315867 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen mediates sex differences in preoptic neuropeptide and pituitary hormone production in medaka.Commun Biol. 2021 Aug 9;4(1):948. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02476-5. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34373576 Free PMC article.
-
Larval Zebrafish Use Olfactory Detection of Sodium and Chloride to Avoid Salt Water.Curr Biol. 2021 Feb 22;31(4):782-793.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.11.051. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33338431 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin 177, prolactin 188, and extracellular osmolality independently regulate the gene expression of ion transport effectors in gill of Mozambique tilapia.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Nov 15;309(10):R1251-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00168.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26377558 Free PMC article.
-
Activities of Amphioxus GH-Like Protein in Osmoregulation: Insight into Origin of Vertebrate GH Family.Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017:9538685. doi: 10.1155/2017/9538685. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Int J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28408927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ball JN, Ensor DM. Effect of prolactin on plasma sodium in the teleost, Poecilia latipinna. J. Endocrinol. 1965;32:269–270. - PubMed
-
- Bayaa M, Vulesevic B, Esbaugh A, Braun M, Ekker ME, Grosell M, Perry SF. The involvement of SLC26 anion transporters in chloride uptake in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2009;212:3283–3295. - PubMed
-
- Bern HA. Functional evolution of prolactin and growth hormone in lower vertebrates. Amer. Zool. 1983;23:663–671.
-
- Bernichtein S, Kayser C, Dillner K, Moulin S, Kopchick JJ, Martial JA, Norstedt G, Isaksson O, Kelly PA, Goffin V. Development of pure prolactin receptor antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:35988–35999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

