Antagonism of SET using OP449 enhances the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and overcomes drug resistance in myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 24436473
- PMCID: PMC3989420
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2575
Antagonism of SET using OP449 enhances the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and overcomes drug resistance in myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: The SET oncoprotein, a potent inhibitor of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), is overexpressed in leukemia. We evaluated the efficacy of SET antagonism in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines, a murine leukemia model, and primary patient samples using OP449, a specific, cell-penetrating peptide that antagonizes SET's inhibition of PP2A.
Experimental design: In vitro cytotoxicity and specificity of OP449 in CML and AML cell lines and primary samples were measured using proliferation, apoptosis, and clonogenic assays. Efficacy of target inhibition by OP449 was evaluated by immunoblotting and PP2A assay. In vivo antitumor efficacy of OP449 was measured in human HL-60 xenografted murine model.
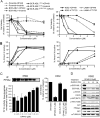
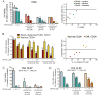
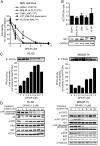
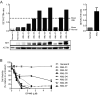
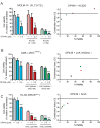
Results: We observed that OP449 inhibited growth of CML cells including those from patients with blastic phase disease and patients harboring highly drug-resistant BCR-ABL1 mutations. Combined treatment with OP449 and ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors was significantly more cytotoxic to K562 cells and primary CD34(+) CML cells. SET protein levels remained unchanged with OP449 treatment, but BCR-ABL1-mediated downstream signaling was significantly inhibited with the degradation of key signaling molecules such as BCR-ABL1, STAT5, and AKT. Similarly, AML cell lines and primary patient samples with various genetic lesions showed inhibition of cell growth after treatment with OP449 alone or in combination with respective kinase inhibitors. Finally, OP449 reduced the tumor burden of mice xenografted with human leukemia cells.
Conclusions: We demonstrate a novel therapeutic paradigm of SET antagonism using OP449 in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of CML and AML.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
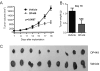
Comment in
-
SETting OP449 into the PP2A-activating drug family.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 15;20(8):2026-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0166. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24634375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A, Byrd J, Deininger MW. The Molecular Biology of the Chronic Leukemias; DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 2011
-
- Birkenkamp KU, Geugien M, Lemmink HH, Kruijer W, Vellenga E. Regulation of constitutive STAT5 phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Leukemia : official journal of the Leukemia Society of America, Leukemia Research Fund, UK. 2001;15:1923–31. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 2006;355:2408–17. - PubMed
-
- Chu S, Xu H, Shah NP, Snyder DS, Forman SJ, Sawyers CL, et al. Detection of BCR-ABL kinase mutations in CD34+ cells from chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission on imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood. 2005;105:2093–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

