Pelvic vascular malformations
- PMID: 24436563
- PMCID: PMC3835586
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1359730
Pelvic vascular malformations
Abstract
Vascular malformations (VMs) comprise a wide spectrum of lesions that are classified by content and flow characteristics. These lesions, occurring in both focal and diffuse forms, can involve any organ and tissue plane and can cause significant morbidity in both children and adults. Since treatment strategy depends on the type of malformation, correct diagnosis and classification of a vascular lesion are crucial. Slow-flow VMs (venous and lymphatic malformations) are often treated by sclerotherapy, whereas fast-flow lesions (arteriovenous malformations) are generally managed with embolization. In addition, some cases of VMs are best treated surgically. This review will present an overview of VMs in the female pelvis as well as a discussion of endovascular therapeutic techniques.
Keywords: arteriovenous malformations; endovascular treatment; interventional radiology; lymphatic malformations; vascular malformations; venous malformations.
Figures
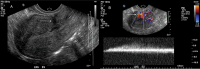
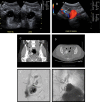
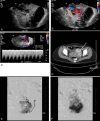
References
-
- Mulliken J B, Glowacki J. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: a classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982;69(3):412–422. - PubMed
-
- Jackson I T, Carreño R, Potparic Z, Hussain K. Hemangiomas, vascular malformations, and lymphovenous malformations: classification and methods of treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993;91(7):1216–1230. - PubMed
-
- Dubois J, Alison M. Vascular anomalies: what a radiologist needs to know. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40(6):895–905. - PubMed
-
- Moukaddam H, Pollak J, Haims A H. MRI characteristics and classification of peripheral vascular malformations and tumors. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;38(6):535–547. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

