Finite element analysis comparison of plate designs in managing fractures involving the mental foramen
- PMID: 24436743
- PMCID: PMC3721010
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1343789
Finite element analysis comparison of plate designs in managing fractures involving the mental foramen
Abstract
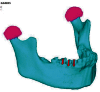
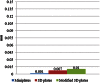
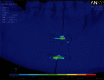
Introduction The aim of the study was to propose an ideal plating design for fractures running through the mental foramen. Methods The study compared three plating designs-two four-hole miniplates, 2 × 2-hole three-dimensional (3D) plate, and modified 2 × 2-hole 3D plate (posterior strut removed)-using finite element analysis. Von Mises stresses generated around the plates and bone were measured, as well as the mobility that is generated between the fracture fragments by applying muscle forces to generate bite force in one test and applying a force of 500 N over the premolars and first molar region in the second test. Results Von Mises stress in bone with miniplates measured 9.24 MPa in test 1 and 131.99 MPa in test 2. The stress with unmodified 3D plates measured 34.9 MPa in test 1 and150.03 MPa in test 2. The stress with modified 3D plates measured 24.98 MPa in test 1 and 150.59 MPa in test 2. Von Mises stress on the plates and screws measured 28.23 MPa, 95.97 MPa, 72.93 MPa in test 1 and 458.63 MPa, 779.01 MPa, 742.39 MPa in test 2 on miniplates, unmodified 3D plates, and modified 3D plates, respectively. The fracture mobility generated in the model with miniplates measured 0.001 mm in test 1 and 0.01 mm in test 2 and 0.007 mm and 0.02 mm in the model with unmodified 3D plates in test 1 and in test 2, respectively. In the model with modified 3D plates, the value was 0.001 mm and 0.01 mm in tests 1 and 2, respectively. Conclusion The ideal plate design is the two-plate technique with minimal stress generation on the bone and the hardware. The modified 3D plate has adequate strength to be used in the region but needs to be studied in detail.
Keywords: Von Mises stresses; finite element analysis; fracture mobility.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Biomechanical effects of different miniplate use on bone and miniplate systems in multiple mandible fracture: A finite element study.Injury. 2024 Dec;55(12):111983. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2024.111983. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Injury. 2024. PMID: 39481256
-
Finite Element Analysis of New Modified Three-dimensional Strut Miniplate versus Conventional Plating in Mandibular Symphysis and Angle Fractures - An In vitro Study.Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Jan-Jun;14(1):71-75. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_205_23. Epub 2024 May 8. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39184404 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison Between Conventional Titanium Miniplates and Indigenous Detachable Custom made 3D Titanium Plates (VAS 3D Bone Plate) for Fixation of Mandibular Fracture in Mental Foramen Region: A Randomized Clinical Trial and Finite Element Analysis.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022 Mar;21(1):211-218. doi: 10.1007/s12663-020-01397-w. Epub 2020 Jun 26. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022. PMID: 35400927 Free PMC article.
-
New fixation method for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: a finite element analysis of sliding hip screw, L-shaped, and L-shaped with medial plate.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 Aug;31(6):1069-1075. doi: 10.1007/s00590-020-02824-x. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 33389052
-
Biomechanical effect of the configuration of screw hole style on locking plate fixation in proximal humerus fracture with a simulated gap: A finite element analysis.Injury. 2016 Jun;47(6):1191-5. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.02.028. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Injury. 2016. PMID: 26975793
References
-
- Champy M, Wilk A, Schnebelen J M. Treatment of mandibular fractures by means of osteosynthesis without intermaxillary immobilization according to F.X. Michelet's technic. Zahn Mund Kieferheilkd Zentralbl. 1975;6(2):339–341. - PubMed
-
- Michelet F X, Deymes J, Dessus B. Osteosynthesis with miniaturized screwed plates in maxilla-facial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg. 1973;6:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Farmand M. Three-dimensional plate fixation of fractures and osteotomies. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 1995;6:39–55.
-
- Lovald S T, Khraishi T, Wagner J, Baack B, Kelly J, Wood J. Comparison of plate screw systems used in mandibular fracture reduction: finite element analysis. J Biomech Eng. 2006;6:654–662. - PubMed
-
- Koolstra J H, van Eijden T M, van Spronsen P H, Weijs W A, Valk J. Computer-assisted estimation of lines of action of human masticatory muscles reconstructed in vivo by means of magnetic resonance imaging of parallel sections. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;6:549–556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
