Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer
- PMID: 24438533
- PMCID: PMC4317941
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12354
Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer
Abstract
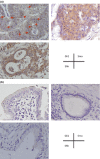
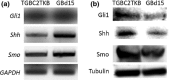
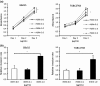
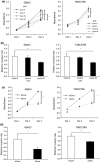
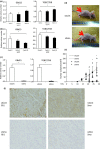
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a particularly deadly type of cancer with a 5-year survival rate of only 10%. New effective therapeutic strategies are greatly needed. Recently, we have shown that Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is reactivated in various types of cancer and is a potential therapeutic target. However, little is known about the biological significance of Hh signaling in human GBC. In this study, we determined whether Hh signaling could be a therapeutic target in GBC. The Hh transcription factor Gli1 was detected in the nucleus of GBC cells but not in the nucleus of normal gallbladder cells. The expression levels of Sonic Hh (Shh) and Smoothened (Smo) in human GBC specimens (n = 37) were higher than those in normal gallbladder tissue. The addition of exogenous Shh ligand augmented the anchor-dependent and anchor-independent proliferation and invasiveness of GBC cells in vitro. In contrast, inhibiting the effector Smo decreased the anchor-dependent and anchor-independent proliferation. Furthermore, the suppression of Smo decreased GBC cell invasiveness through the inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and inhibited the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In a xenograft model, tumor volume in Smo siRNA-transfected GBC cells was significantly lower than in control tumors. These results suggest that Hh signaling is elevated in GBC and may be involved in the acquisition of malignant phenotypes, and that Hh signaling may be a potential therapeutic target for GBC.
Keywords: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Hedgehog; Smo protein; gallbladder cancer; matrix metalloproteinase.
© 2014 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


References
-
- Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC, Sharma ID. Carcinoma of the gallbladder. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:167–76. - PubMed
-
- Glauser PM, Strub D, Käser SA, Mattiello D, Rieben F, Maurer CA. Incidence, management, and outcome of incidental gallbladder carcinoma: analysis of the database of the Swiss association of laparoscopic and thoracoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:2281–6. - PubMed
-
- Gourgiotis S, Kocher HM, Solaini L, Yarollahi A, Tsiambas E, Salemis NS. Gallbladder cancer. Am J Surg. 2008;196:252–64. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–87. - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Kai M, Odate S, et al. Hypoxia activates the hedgehog signaling pathway in a ligand-independent manner by upregulation of Smo transcription in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:1144–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

