Ultra high-resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis and management of ocular surface squamous neoplasia
- PMID: 24439046
- PMCID: PMC3934962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtos.2013.11.001
Ultra high-resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis and management of ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Abstract
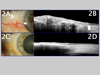
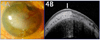
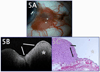
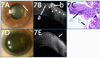
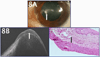
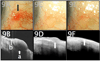
The development of optical coherence tomography (OCT) technology has helped to usher in a new era of in vivo diagnostic imaging of the eye. The utilization of OCT for imaging of the anterior segment and ocular surface has evolved from time-domain devices to spectral-domain devices with greater penetrance and resolution, providing novel images of anterior segment pathology to assist in diagnosis and management of disease. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) is one such pathology that has proven demonstrable by certain anterior segment OCT machines, specifically the newer devices capable of performing ultra high-resolution OCT (UHR-OCT). Distinctive features of OSSN on high resolution OCT allow for diagnosis and differentiation from other ocular surface pathologies. Subtle findings on these images help to characterize the OSSN lesions beyond what is apparent with the clinical examination, providing guidance for clinical management. The purpose of this review is to examine the published literature on the utilization of UHR-OCT for the diagnosis and management of OSSN, as well as to report novel uses of this technology and potential directions for its future development.
Keywords: 5-FU; 5-Fluorouracil; AS-OCT; Anterior segment optical coherence tomography; FD-OCT; Fourier-domain OCT; Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography; HIV; HR-OCT; High-resolution optical coherence tomography; Human immunodeficiency virus; IFN; Interferon; LASIK; LSCD; Laser in situ keratomileusis; Limbal stem cell deficiency; MMC; Mitomycin C; OCT; OSSN; Ocular surface squamous neoplasia; Optical coherence tomography; SD-OCT; SL-OCT; SLE; SS-OCT; Slit lamp examination; Slit lamp optical coherence tomography; Spectral domain optical coherence tomography; Swept-source optical coherence tomography; TD-OCT; Time-domain optical coherence tomography; UBM; UHR-OCT; Ultra high-resolution optical coherence tomography; Ultrasound biomicroscopy; anterior segment OCT; high-resolution OCT; ocular surface squamous neoplasia; optical coherence tomography (OCT); slit lamp OCT; spectral domain OCT; swept-source OCT; time-domain OCT; ultra high-resolution OCT.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anterior Segment Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography in Ocular Surface Tumors and Simulating Lesions and Correlation With Histopathologic Diagnosis.Cornea. 2025 Mar 28;44(7):806-818. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000003856. Cornea. 2025. PMID: 40152549
-
Ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography for differentiation of ocular surface squamous neoplasia and pterygia.Ophthalmology. 2012 Mar;119(3):481-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.08.028. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Ophthalmology. 2012. PMID: 22154538
-
Diagnosis of ocular surface lesions using ultra-high-resolution optical coherence tomography.Ophthalmology. 2013 May;120(5):883-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.10.025. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Ophthalmology. 2013. PMID: 23347984 Free PMC article.
-
Medical treatment for ocular surface squamous neoplasia.Eye (Lond). 2023 Apr;37(5):885-893. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02434-x. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Eye (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36754986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia: management and outcomes.Eye (Lond). 2021 Jun;35(6):1562-1573. doi: 10.1038/s41433-021-01422-3. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Eye (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33564137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole exome profiling and mutational analysis of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia.Ocul Surf. 2020 Oct;18(4):627-632. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Ocul Surf. 2020. PMID: 32717381 Free PMC article.
-
Non-malignant conjunctival epithelial masses with ocular surface squamous neoplasia-like optical coherence tomography features.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 May;41(5):1827-1834. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01743-y. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33694094 Free PMC article.
-
Ability of novice clinicians to interpret high-resolution optical coherence tomography for ocular surface lesions.Can J Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr;53(2):150-154. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Can J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29631827 Free PMC article.
-
Use of High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography in the Surgical Management of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia: A Pilot Study.Am J Ophthalmol. 2019 Oct;206:17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2019.05.017. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31163136 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound in ocular oncology: Technical advances, clinical applications, and limitations.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 May;248(5):371-379. doi: 10.1177/15353702231169539. Epub 2023 May 22. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 37212384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Izatt JA, Hee MR, Swanson EA, et al. Micrometer-scale resolution imaging of the anterior eye in vivo with optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994;112:1584–1589. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Abou Shousha M, Perez VL, et al. Ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography for imaging the anterior segment of the eye. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2011;42:S15–s27. - PubMed
-
- Grieve K, Paques M, Dubois A, et al. Ocular tissue imaging using ultrahigh-resolution, full-field optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:4126–4131. - PubMed
-
- Simpson T, Fonn D. Optical coherence tomography of the anterior segment. Ocul Surf. 2008;6:117–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

