The cis-regulatory effect of an Alzheimer's disease-associated poly-T locus on expression of TOMM40 and apolipoprotein E genes
- PMID: 24439168
- PMCID: PMC4098029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.08.280
The cis-regulatory effect of an Alzheimer's disease-associated poly-T locus on expression of TOMM40 and apolipoprotein E genes
Abstract
Background: We investigated the genomic region spanning the Translocase of the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane 40-kD (TOMM40) and Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genes, that has been associated with the risk and age of onset of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) to determine whether a highly polymorphic, intronic poly-T within this region (rs10524523; hereafter, 523) affects expression of the APOE and TOMM40 genes. Alleles of this locus are classified as S, short; L, long; and VL, very long based on the number of T residues.
Methods: We evaluated differences in APOE messenger RNA (mRNA) and TOMM40 mRNA levels as a function of the 523 genotype in two brain regions from APOE ε3/ε3 white autopsy-confirmed LOAD cases and normal controls. We further investigated the effect of the 523 locus in its native genomic context using a luciferase expression system.
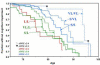
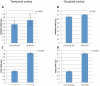
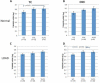
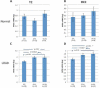
Results: The expression of both genes was significantly increased with disease. Mean expression of APOE and TOMM40 mRNA levels were higher in VL homozygotes compared with S homozygotes in the temporal and occipital cortexes from normal and LOAD cases. Results of a luciferase reporter system were consistent with the human brain mRNA analysis; the 523 VL poly-T resulted in significantly higher expression than the S poly-T. Although the effect of poly-T length on reporter expression was the same in HepG2 hepatoma and SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, the magnitude of the effect was greater in the neuroblastoma than in the hepatoma cells, which implies tissue-specific modulation of the 523 poly-T.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the 523 locus may contribute to LOAD susceptibility by modulating the expression of TOMM40 and/or APOE transcription.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Apolipoprotein E; Messenger RNA expression; Poly-T polymorphism; TOMM40; Transcription regulation.
Copyright © 2014 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of TOMM40 poly-T length on gray matter volume and cognition in middle-aged persons with APOE ε3/ε3 genotype.Alzheimers Dement. 2011 Jul;7(4):456-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.11.012. Alzheimers Dement. 2011. PMID: 21784354 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease susceptibility genes APOE and TOMM40, and brain white matter integrity in the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Jun;35(6):1513.e25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24508314 Free PMC article.
-
An inherited variable poly-T repeat genotype in TOMM40 in Alzheimer disease.Arch Neurol. 2010 May;67(5):536-41. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.88. Arch Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20457951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TOMM40 intron 6 poly-T length, age at onset, and neuropathology of AD in individuals with APOE ε3/ε3.Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Sep;9(5):554-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Alzheimers Dement. 2013. PMID: 23183136 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the TOMM40 poly-T alleles on Alzheimer's disease phenotypes.Alzheimers Dement. 2018 May;14(5):692-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2018. PMID: 29524426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical testing in transcriptomic-neuroimaging studies: A how-to and evaluation of methods assessing spatial and gene specificity.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Feb 15;43(3):885-901. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25711. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 34862695 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria as Potential Targets in Alzheimer Disease Therapy: An Update.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 23;10:902. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00902. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31507410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of pleiotropic genetic effects on cognitive impairment, systemic inflammation, and plasma lipids in the Health and Retirement Study.Neurobiol Aging. 2019 Aug;80:173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.10.028. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 31201950 Free PMC article.
-
TOMM40 RNA Transcription in Alzheimer's Disease Brain and Its Implication in Mitochondrial Dysfunction.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 6;12(6):871. doi: 10.3390/genes12060871. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204109 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Mechanisms of Selective PPARγ Modulators in Alzheimer's Disease.PPAR Res. 2018 Oct 21;2018:2010675. doi: 10.1155/2018/2010675. eCollection 2018. PPAR Res. 2018. PMID: 30420872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caselli RJ, et al. TOMM40, APOE and age of onset of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's and Dementia. 2010;6:S202.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

