Blood flow reduction in breast tissue due to mammographic compression
- PMID: 24439328
- PMCID: PMC4393946
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.10.009
Blood flow reduction in breast tissue due to mammographic compression
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: This study measures hemodynamic properties such as blood flow and hemoglobin concentration and oxygenation in the healthy human breast under a wide range of compressive loads. Because many breast-imaging technologies derive contrast from the deformed breast, these load-dependent vascular responses affect contrast agent-enhanced and hemoglobin-based breast imaging.
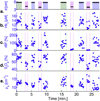
Methods: Diffuse optical and diffuse correlation spectroscopies were used to measure the concentrations of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin, lipid, water, and microvascular blood flow during axial breast compression in the parallel-plate transmission geometry.
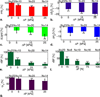
Results: Significant reductions (P < .01) in total hemoglobin concentration (∼30%), blood oxygenation (∼20%), and blood flow (∼87%) were observed under applied pressures (forces) of up to 30 kPa (120 N) in 15 subjects. Lipid and water concentrations changed <10%.
Conclusions: Imaging protocols based on injected contrast agents should account for variation in tissue blood flow due to mammographic compression. Similarly, imaging techniques that depend on endogenous blood contrasts will be affected by breast compression during imaging.
Keywords: Mammographic compression; blood flow; breast cancer; breast imaging; diffuse optics.
Copyright © 2014 AUR. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. A. C. S. B. C. A. Group. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA-Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75–89. - PubMed
-
- Niklason LT, Christian BT, Niklason LE, et al. Digital tomosynthesis in breast imaging. Radiology. 1997;205:399–406. - PubMed
-
- O’Hagan JJ, Samani A. Measurement of the hyperelastic properties of 44 pathological ex vivo breast tissue samples. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54:2557. - PubMed
-
- O’Hagan JJ, Samani A. Measurement of the hyperelastic properties of tissue slices with tumour inclusion. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53:7087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-EB002109/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA126187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL007915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA105480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99/R00-CA126187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR002305/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060653/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA126187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54CA105480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR002305/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002109/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

