Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4
- PMID: 24439385
- PMCID: PMC4076414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4
Abstract
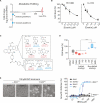
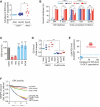
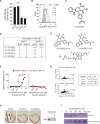
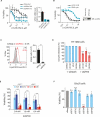
Ferroptosis is a form of nonapoptotic cell death for which key regulators remain unknown. We sought a common mediator for the lethality of 12 ferroptosis-inducing small molecules. We used targeted metabolomic profiling to discover that depletion of glutathione causes inactivation of glutathione peroxidases (GPXs) in response to one class of compounds and a chemoproteomics strategy to discover that GPX4 is directly inhibited by a second class of compounds. GPX4 overexpression and knockdown modulated the lethality of 12 ferroptosis inducers, but not of 11 compounds with other lethal mechanisms. In addition, two representative ferroptosis inducers prevented tumor growth in xenograft mouse tumor models. Sensitivity profiling in 177 cancer cell lines revealed that diffuse large B cell lymphomas and renal cell carcinomas are particularly susceptible to GPX4-regulated ferroptosis. Thus, GPX4 is an essential regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Brigelius-Flohé R, Maiorino M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1830:3289–3303. - PubMed
-
- Cotter TG. Apoptosis and cancer: the genesis of a research field. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009;9:501–507. - PubMed
-
- Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005;1:112–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 CA148399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10RR025431-01A1/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01-CA70823-15/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025431/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5R01CA097061/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA161061/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM085081/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2-CA148399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01GM085081/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA177591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097061/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA070823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA161061/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

