Non-length-dependent and length-dependent small-fiber neuropathies associated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: expanding the spectrum of neurological disease associated with TNF-inhibitors
- PMID: 24439654
- PMCID: PMC4605274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.10.007
Non-length-dependent and length-dependent small-fiber neuropathies associated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: expanding the spectrum of neurological disease associated with TNF-inhibitors
Abstract
Objective: Small-fiber neuropathy causes severe burning pain, requires diagnostic approaches such as skin biopsy, and encompasses two subtypes based on distribution of neuropathic pain. Such biopsy-proven subtypes of small-fiber neuropathies have not been previously described as complications of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor therapy.
Methods: We therefore characterized clinical and skin biopsy findings in three rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who developed small-fiber neuropathies associated with TNF-inhibitors. We also conducted a systematic review of the literature to characterize subtypes of neuropathies previously reported in association with TNF-inhibitor therapy.
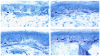
Results: Two patients presented with a "non-length-dependent" small-fiber neuropathy, experiencing unorthodox patterns of burning pain affecting the face, torso, and proximal extremities. Abnormal skin biopsy findings were limited to the proximal thigh, which is a marker of proximal-most dorsal root ganglia degeneration. In contrast, one patient presented with a "length-dependent" small-fiber neuropathy, experiencing burning pain only in the feet. Abnormal skin biopsy findings were limited to the distal feet, which is a marker of distal-most axonal degeneration. One patient developed a small-fiber neuropathy in the context of TNF-inhibitor-induced lupus. In all patients, neuropathies occurred during TNF-inhibitor-induced remission of RA disease activity and improved on withdrawal of TNF-inhibitors.
Conclusions: We describe a spectrum of small-fiber neuropathies not previously reported in association with TNF-inhibitor therapy, with clinical and skin biopsy findings suggestive of dorsal root ganglia as well as axonal degeneration. The development of small-fiber neuropathies during inactive joint disease and improvement of neuropathic pain upon withdrawal of TNF-inhibitor suggest a causative role of TNF-inhibitors.
© 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF alpha antagonist-induced lupus-like syndrome: report and review of the literature with implications for treatment with alternative TNF alpha antagonists.Int J Dermatol. 2011 May;50(5):619-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.04871.x. Int J Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21506984 Review.
-
Risk of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-alpha agents.JAMA. 2009 Feb 18;301(7):737-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.146. JAMA. 2009. PMID: 19224750
-
Cutaneous vasculitis induced by TNF inhibitors: a report of three cases.Mod Rheumatol. 2010 Feb;20(1):86-9. doi: 10.1007/s10165-009-0232-7. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Mod Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 19812889
-
Survival of TNF-alpha antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis: a long-term study.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012 Jan-Feb;30(1):31-8. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22153557
-
Update on the Japanese guidelines for the use of infliximab and etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17(6):451-8. doi: 10.1007/s10165-007-0626-3. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Mod Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 18084695 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of small fiber neuropathy and post treatment Lyme disease syndrome.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 12;14(2):e0212222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212222. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30753241 Free PMC article.
-
Small Fiber Neuropathy Associated with Post-COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Vaccination Arthritis: A Rare Post-Infective Syndrome or a New-Onset Disease?J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 25;14(8):789. doi: 10.3390/jpm14080789. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39201981 Free PMC article.
-
IVIg for apparently autoimmune small-fiber polyneuropathy: first analysis of efficacy and safety.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2018 Jan 8;11:1756285617744484. doi: 10.1177/1756285617744484. eCollection 2018. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2018. PMID: 29403541 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Statins with Sensory and Autonomic Ganglionopathy.Front Aging Neurosci. 2015 Oct 7;7:191. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00191. eCollection 2015. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26500548 Free PMC article.
-
Novel three-dimensional analysis method for accurate evaluation of cutaneous small sensory nerve fibers in mice.J Toxicol Pathol. 2025 Apr;38(2):167-175. doi: 10.1293/tox.2024-0085. Epub 2025 Jan 2. J Toxicol Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40190624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shin IS, Baer AN, Kwon HJ, Papadopoulos EJ, Siegel JN. Guillain–Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes occurring with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1429–34. - PubMed
-
- Stübgen JP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2008;37:281–92. - PubMed
-
- Bosch X, Saiz A, Ramos-Casals M. Monoclonal antibody therapy-associated neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:165. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Alvarez R, Perez-de-Lis M, Ramos-Casals M On behalf of the BIOGEAS study group. Biologics-induced autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25:56–64. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum J. Peripheral nervous system manifestations of Sjogren syndrome: clinical patterns, diagnostic paradigms, etiopathogenesis, and therapeutic strategies. Neurologist. 2010;16:287–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

