Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and liver diseases
- PMID: 24440671
- PMCID: PMC3996054
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.020
Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and liver diseases
Abstract
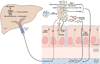
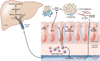
The human intestine harbors a diverse community of microbes that promote metabolism and digestion in their symbiotic relationship with the host. Disturbance of its homeostasis can result in disease. We review factors that disrupt intestinal homeostasis and contribute to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, steatohepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Liver disease has long been associated with qualitative and quantitative (overgrowth) dysbiotic changes in the intestinal microbiota. Extrinsic factors, such as the Western diet and alcohol, contribute to these changes. Dysbiosis results in intestinal inflammation, a breakdown of the intestinal barrier, and translocation of microbial products in animal models. However, the contribution of the intestinal microbiome to liver disease goes beyond simple translocation of bacterial products that promote hepatic injury and inflammation. Microbial metabolites produced in a dysbiotic intestinal environment and host factors are equally important in the pathogenesis of liver disease. We review how the combination of liver insult and disruptions in intestinal homeostasis contribute to liver disease.
Keywords: Alcoholic Steatohepatitis; Endotoxin; Microbiota.
Copyright © 2014 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Williams CD, Stengel J, Asike MI, Torres DM, Shaw J, Contreras M, Landt CL, Harrison SA. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:124–131. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell S, Argo C. The natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis. 2010;28:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM, Probert CS, Ratcliffe NM, Smith S, Greenwood R, Sikaroodi M, Lam V, Crotty P, Bailey J, Myers RP, Rioux KP. Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:868–875. e3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

