Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK pathway to induce cytoskeleton remodeling in nucleus pulposus cells
- PMID: 24441571
- PMCID: PMC3907862
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15011176
Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK pathway to induce cytoskeleton remodeling in nucleus pulposus cells
Abstract
Hyperleptinemia is implicated in obesity-associated lumbar disc degeneration. Nevertheless, the effect of leptin on the intracellular signaling of nucleus pulposus cells is not clear. The current study sought to delineate the possible involvement of the RhoA/ROCK pathway in leptin-mediated cytoskeleton reorganization in nucleus pulposus cells. Nucleus pulposus cells isolated from scoliosis patients were treated with 10 ng/mL of leptin. Fluorescent resonance energy transfer analysis was used to determine the activation of RhoA signaling in nucleus pulposus cells. The protein expression of LIMK1 and cofilin-2 were analyzed by western blot analysis. F-actin cytoskeletal reorganization was assessed by rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin immunoprecipitation. Leptin induced F-actin reorganization and stress fiber formation in nucleus pulposus cells, accompanied by localized RhoA activation and phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin. The RhoA inhibitor C3 exoenzyme or the ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 potently attenuated the effects of leptin on F-actin reorganization and stress fiber formation. Both inhibitors also prevented leptin-induced phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin-2. Our study demonstrated that leptin activated the RhoA/ROCK/LIMK/cofilin-2 cascade to induce cytoskeleton reorganization in nucleus pulposus cells. These findings may provide novel insights into the pathogenic mechanism of obesity-associated lumbar disc degeneration.
Figures


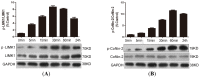

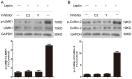

References
-
- Haslam D.W., James W.P. Obesity. Lancet. 2005;366:1197–1209. - PubMed
-
- Samartzis D., Karppinen J., Mok F., Fong D.Y., Luk K.D., Cheung K.M. A population-based study of juvenile disc degeneration and its association with overweight and obesity, low back pain, and diminished functional status. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2011;93:662–670. - PubMed
-
- Bostman O.M. Prevalence of obesity among patients admitted for elective orthopaedic surgery. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1994;18:709–713. - PubMed
-
- L’Allemand D., Schmidt S., Rousson V., Brabant G., Gasser T., Gruters A. Associations between body mass, leptin, IGF-I and circulating adrenal androgens in children with obesity and premature adrenarche. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002;146:537–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

