The effect of type 1 IFN on human aortic endothelial cell function in vitro: relevance to systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 24444308
- PMCID: PMC4015474
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2013.0016
The effect of type 1 IFN on human aortic endothelial cell function in vitro: relevance to systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
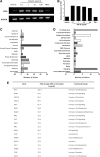
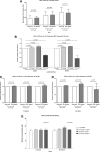
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The etiopathogenesis of premature CVD is not fully understood, but recently interferon-alpha (IFNα) has been implicated as a contributing factor. Since IFNα has been associated with both disease activity and endothelial dysfunction in lupus patients, we aimed to determine whether IFNα has direct effects on human aortic endothelial cell (HAoEC) function in vitro. We studied the function of IFNα2b-treated HAoECs in terms of cell proliferation, capillary-like network formation, and nitric oxide (NO) generation. Changes in gene expression were also analyzed using an exon gene array. IFNα2b regulated the expression of 198 genes, including recognized interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Gene ontology analysis showed over-representation of genes involved in antigen presentation and host response to virus but no significant changes in clusters of genes recognized as important in endothelial cell activation or dysfunction. HAoEC proliferation, tubule formation, and NO bioavailability were unchanged, suggesting that IFNα in isolation does not have a direct impact on aortic endothelial cell function.
Figures


References
-
- Aird WC. 2007. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium. Circ Res 100(2):158–173 - PubMed
-
- Baechler EC, Batiwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, Shark KB, Grande WJ, Hughes KM, Kapur V, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. 2003. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100(5):2610–2615 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
