Logistics of Guinea worm disease eradication in South Sudan
- PMID: 24445199
- PMCID: PMC3945682
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0110
Logistics of Guinea worm disease eradication in South Sudan
Abstract
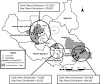
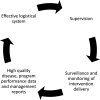
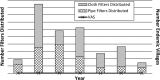
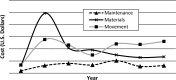
From 2006 to 2012, the South Sudan Guinea Worm Eradication Program reduced new Guinea worm disease (dracunculiasis) cases by over 90%, despite substantial programmatic challenges. Program logistics have played a key role in program achievements to date. The program uses disease surveillance and program performance data and integrated technical-logistical staffing to maintain flexible and effective logistical support for active community-based surveillance and intervention delivery in thousands of remote communities. Lessons learned from logistical design and management can resonate across similar complex surveillance and public health intervention delivery programs, such as mass drug administration for the control of neglected tropical diseases and other disease eradication programs. Logistical challenges in various public health scenarios and the pivotal contribution of logistics to Guinea worm case reductions in South Sudan underscore the need for additional inquiry into the role of logistics in public health programming in low-income countries.
Figures




References
-
- Hopkins DR, Ruiz-Tiben E, Diallo N, Withers C, Maguire J. Dracunculiasis eradication: and now, Sudan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:415–422. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Progress toward global eradication of Dracunculiasis, January 2005–May 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56:813–817. - PubMed
-
- Wickett J, Carrasco P. Logistics in smallpox: the legacy. Vaccine. 2011;29((Suppl 4)):D131–D134. - PubMed
-
- Ghiana G, Laporte G, Musmanno R. Introduction to Logistical Systems Planning and Control. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2004.
-
- World Health Organization Conclusions of the meeting of the Technical Advisory Group on the Global Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis, November 2007. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2008;83:345. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

