The bioconcentration and degradation of nonylphenol and nonylphenol polyethoxylates by Chlorella vulgaris
- PMID: 24445260
- PMCID: PMC3907867
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15011255
The bioconcentration and degradation of nonylphenol and nonylphenol polyethoxylates by Chlorella vulgaris
Abstract
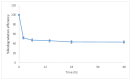
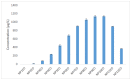
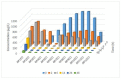
Nonylphenol polyethoxylates (NPnEOs), a major class of nonionic surfactants, can easily enter into aquatic environments through various pathways due to their wide applications, which leads to the extensive existence of their relative stable metabolites, namely nonylphenol (NP) and mono- to tri-ethoxylates. This study investigated the bioconcentration and degradation of NP and NPnEO oligomers (n = 1-12) by a green algae, Chlorella vulgaris. Experimental results showed that C. vulgaris can remove NP from water phase efficiently, and bioconcentration and degradation accounted for approximately half of its loss, respectively, with a 48 h BCF (bioconcentration factor) of 2.42 × 10(3). Moreover, C. vulgaris could concentrate and degrade NPnEOs, distribution profiles of the series homologues of the NPnEOs in algae and water phase were quite different from the initial homologue profile. The 48 h BCF of the NPnEO homologues increased with the length of the EO chain. Degradation extent of total NPnEOs by C. vulgaris was 95.7%, and only 1.1% remained in water phase, and the other 3.2% remained in the algal cells. The algae removed the NPnEOs mainly through degradation. Due to rapid degradation, concentrations of the long chain NPnEO homologous in both water (n ≥ 2) and the algal phase (n ≥ 5) was quite low at the end of a 48 h experiment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nonylphenol polyethoxylate degradation in aqueous waste by the use of batch and continuous biofilm bioreactors.Water Res. 2009 Jul;43(12):2977-88. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.04.011. Epub 2009 Apr 19. Water Res. 2009. PMID: 19447463
-
Removal and biodegradation of nonylphenol by different Chlorella species.Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;63(5-12):445-51. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.03.030. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011. PMID: 21507429
-
Occurrence of nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylate surfactants and nonylphenol carboxylic acids in wastewater in Japan.Water Sci Technol. 2006;53(11):27-33. doi: 10.2166/wst.2006.334. Water Sci Technol. 2006. PMID: 16862771
-
Occurrence and biodegradation of nonylphenol in the environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(1):491-505. doi: 10.3390/ijms13010491. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22312266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fate of Alkyl Polyglucosides in the Environment.J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Jan-Feb;72(1):91-98. J Cosmet Sci. 2021. PMID: 35349428 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioaccumulation and in vivo tracking of radiolabeled 4-nonylphenol in mice.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 14;14(12):8578-8582. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08743c. eCollection 2024 Mar 6. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38487519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Staples C.A., Weeks J., Hall J.F., Naylor C.G. Evaluation of aquatic toxicity and bioaccumulation of C8- and C9- alkylphenol ethoxylates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998;17:2470–2480.
-
- Bettinetti R., Cuccato D., Galassi S., Provini A. Toxicity of 4-nonylphenol in spiked sediment to three populations of Chironomus riparius. Chemosphere. 2002;46:201–207. - PubMed
-
- Kannan K., Keith T.L., Naylor C.G., Staples C.A., Snyder S.A., Giesy J.P. Nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates in fish, sediment, and water from the Kalamazoo River, Michigan. Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 2003;44:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Ying G.-G., Williams B., Kookana R. Environmental fate of alkylphenols and alkylphenol ethoxylates—A review. Environ. Int. 2002;28:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Vazquez-Duhalt R., Marquez-Rocha F., Ponce E., Licea A.F., Viana M.T. Nonylphenol, an integrated vision of a pollutant. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2005;4:1–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

