Thiopeptide antibiotics: retrospective and recent advances
- PMID: 24445304
- PMCID: PMC3917276
- DOI: 10.3390/md12010317
Thiopeptide antibiotics: retrospective and recent advances
Abstract
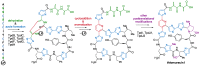
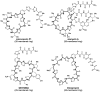
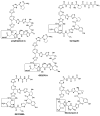
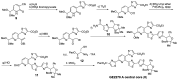
Thiopeptides, or thiazolyl peptides, are a relatively new family of antibiotics that already counts with more than one hundred different entities. Although they are mainly isolated from soil bacteria, during the last decade, new members have been isolated from marine samples. Far from being limited to their innate antibacterial activity, thiopeptides have been found to possess a wide range of biological properties, including anticancer, antiplasmodial, immunosuppressive, etc. In spite of their ribosomal origin, these highly posttranslationally processed peptides have posed a fascinating synthetic challenge, prompting the development of various methodologies and strategies. Regardless of their limited solubility, intensive investigations are bringing thiopeptide derivatives closer to the clinic, where they are likely to show their veritable therapeutic potential.
Figures

















Similar articles
-
Thiopeptide engineering: a multidisciplinary effort towards future drugs.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Jun 23;53(26):6602-16. doi: 10.1002/anie.201307288. Epub 2014 May 23. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 24861213 Review.
-
Introduction to Thiopeptides: Biological Activity, Biosynthesis, and Strategies for Functional Reprogramming.Cell Chem Biol. 2020 Aug 20;27(8):1032-1051. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Cell Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32698017 Review.
-
Thiopeptides: antibiotics with unique chemical structures and diverse biological activities.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021 Mar;74(3):161-175. doi: 10.1038/s41429-020-00387-x. Epub 2020 Dec 21. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 33349675 Review.
-
Molecular determinants of microbial resistance to thiopeptide antibiotics.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 May 26;132(20):6973-81. doi: 10.1021/ja909317n. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20441189
-
Post-translational modifications involved in the biosynthesis of thiopeptide antibiotics.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Apr 18;15(16):3376-3390. doi: 10.1039/c7ob00466d. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28358161 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Biosynthesis of the Core Scaffold of the Thiopeptide Thiomuracin.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Dec 30;137(51):16012-5. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10194. Epub 2015 Dec 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 26675417 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis of NosM Leader Peptide Reveals Important Elements in Nosiheptide Biosynthesis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Feb 1;83(4):e02880-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02880-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27913416 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Based Characterization of a Plasmid-Associated Micrococcin P1 Biosynthetic Gene Cluster and Virulence Factors in Mammaliicoccus sciuri IMDO-S72.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Feb 22;88(4):e0208821. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02088-21. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34936836 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive genome analysis of Lentzea reveals repertoire of polymer-degrading enzymes and bioactive compounds with clinical relevance.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12427-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589875 Free PMC article.
-
RiPP antibiotics: biosynthesis and engineering potential.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2018 Oct;45:61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.02.010. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29533845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumar N. Lantibiotics a novel antimicrobial agents: A review. Pharma Sci. Monit. 2012;3:2990–3009.
-
- LaMarche M.J., Leeds J.A., Amaral A., Brewer J.T., Bushell S.M., Deng G., Dewhurst J.M., Ding J., Dzink-fox J., Gamber G., et al. Discovery of LFF571: An investigational agent for Clostridium difficile infection. J. Med. Chem. 2012;6:2376–2387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

