Docosahexaenoic acid reverses angiotensin II-induced RECK suppression and cardiac fibroblast migration
- PMID: 24447911
- PMCID: PMC3951845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.005
Docosahexaenoic acid reverses angiotensin II-induced RECK suppression and cardiac fibroblast migration
Abstract
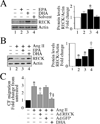
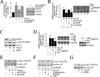
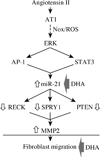
The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 fatty acids) eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have been reported to inhibit or delay the progression of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial fibrosis. Recently we reported that angiotensin II (Ang II) promotes cardiac fibroblast (CF) migration by suppressing the MMP regulator reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK), through a mechanism dependent on AT1, ERK, and Sp1. Here we investigated the role of miR-21 in Ang II-mediated RECK suppression, and determined whether the ω-3 fatty acids reverse these effects. Ang II induced miR-21 expression in primary mouse cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) via ERK-dependent AP-1 and STAT3 activation, and while a miR-21 inhibitor reversed Ang II-induced RECK suppression, a miR-21 mimic inhibited both RECK expression and Ang II-induced CF migration. Moreover, Ang II suppressed the pro-apoptotic PTEN, and the ERK negative regulator Sprouty homologue 1 (SPRY1), but induced the metalloendopeptidase MMP2, all in a manner that was miR-21-dependent. Further, forced expression of PTEN inhibited Akt phosphorylation, Sp1 activation, and MMP2 induction. Notably, while both EPA and DHA reversed Ang II-mediated RECK suppression, DHA appeared to be more effective, and reversed Ang II-induced miR-21 expression, RECK suppression, MMP2 induction, and CF migration. These results indicate that Ang II-induced CF migration is differentially regulated by miR-21-mediated MMP induction and RECK suppression, and that DHA has the potential to upregulate RECK, and therefore may exert potential beneficial effects in cardiac fibrosis.
Keywords: Fibrosis; MicroRNA; PTEN; RECK; SPRY1; ω−3 lipids.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling.Cell Signal. 2021 Jul;83:109993. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109993. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33781845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II stimulates cardiac fibroblast migration via the differential regulation of matrixins and RECK.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Dec;65:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.09.015. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24095877 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetyltransferase inhibitors Trichostatin A and Mocetinostat differentially regulate MMP9, IL-18 and RECK expression, and attenuate Angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibroblast migration and proliferation.Hypertens Res. 2016 Oct;39(10):709-716. doi: 10.1038/hr.2016.54. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Hypertens Res. 2016. PMID: 27278287
-
RECK suppresses interleukin-17/TRAF3IP2-mediated MMP-13 activation and human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Dec;234(12):22242-22259. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28792. Epub 2019 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31074012 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Updates on the Therapeutic Prospects of Reversion-Inducing Cysteine-Rich Protein with Kazal Motifs (RECK) in Liver Injuries.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 12;24(24):17407. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417407. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Minocycline inhibits PDGF-BB-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by reversing miR-221- and -222-mediated RECK suppression.Cell Signal. 2019 May;57:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 30716386 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipids Mediators on Cardiac Fibrosis via NRF2 Activation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 10;9(12):1259. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121259. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33321955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of microRNAs in Renin-Angiotensin-System-Induced Cardiac Remodelling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 30;22(9):4762. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094762. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling.Cell Signal. 2021 Jul;83:109993. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109993. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33781845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of RECK in Hepatobiliary Neoplasia Reveals Its Therapeutic Potential in NASH.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 20;12:770740. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.770740. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker AH, Edwards DR, Murphy G. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 19):3719–3727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

