Transcriptional repression of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) Pseudoreceptor BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) by Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) p50 enhances TGF-β signaling in hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 24448807
- PMCID: PMC3945368
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.543769
Transcriptional repression of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) Pseudoreceptor BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) by Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) p50 enhances TGF-β signaling in hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
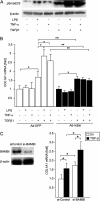
TLR4 signaling induces down-regulation of the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI), which enhances TGF-β signaling during hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. We investigated the mechanism by which TLR4 signaling down-regulates BAMBI expression in HSCs and found that TLR4- and TNF-α-mediated BAMBI down-regulation is dependent on regulation of BAMBI promoter activity through the interaction with NF-κBp50 and HDAC1 in HSCs. Bambi was predominantly expressed in HSCs, at high levels in quiescent HSCs but at low levels in in vivo-activated and LPS-stimulated HSCs. In human HSCs, BAMBI expression was down-regulated in response to LPS and TNF-α. A BAMBI reporter assay demonstrated that the regulatory element to repress BAMBI transcription is located between 3384 and 1560 bp upstream from the transcription start site. LPS stimulation down-regulated BAMBI expression in cells with NF-κBp65 knockdown. However, it failed to down-regulate BAMBI in cells with inactivation of NF-κB or NF-κBp50 silencing, indicating that NF-κBp50 is a factor for BAMBI down-regulation. ChIP analysis revealed that LPS and TNF-α induced binding of the NF-κBp50/p50 homodimer to the BAMBI promoter region. We also found that HDAC1 is bound to this region as part of the NF-κBp50-HDAC1 complex, repressing transcriptional activity of the BAMBI promoter. Finally, we confirmed that LPS does not repress BAMBI reporter activity using a BAMBI reporter construct with a mutation at 3166 bp upstream of the coding region. In summary, our study demonstrates that LPS- and TNF-α-induced NF-κBp50-HDAC1 interaction represses BAMBI transcriptional activity, which contributes to TLR4-mediated enhancement of TGF-β signaling in HSCs during liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Hepatic Stellate Cells; Lipopolysaccharide (LPS); NF-κB; Toll-like Receptors (TLR); Transcription Promoter; Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β).
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-942 mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating BAMBI expression in human liver fibrosis.Arch Toxicol. 2018 Sep;92(9):2935-2946. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2278-9. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30097701 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II facilitates fibrogenic effect of TGF-β1 through enhancing the down-regulation of BAMBI caused by LPS: a new pro-fibrotic mechanism of angiotensin II.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e76289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076289. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155898 Free PMC article.
-
Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate BDL-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28864168
-
Expression and Function of BMP and Activin Membrane-Bound Inhibitor (BAMBI) in Chronic Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 9;24(4):3473. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043473. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and application strategies of miRNA‑146a regulating inflammation and fibrosis at molecular and cellular levels (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Jan;51(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5210. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36484394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β Sustains Tumor Progression through Biochemical and Mechanical Signal Transduction.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Jun 14;10(6):199. doi: 10.3390/cancers10060199. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29903994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum endocan as a survival predictor for patients with liver cirrhosis.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(8):427-30. doi: 10.1155/2015/153805. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26669300 Free PMC article.
-
A meritorious integrated medical regimen for hepatic fibrosis and its complications via the systematic review and meta-analysis for Dahuang Zhechong pill-based therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 14;9:920062. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.920062. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36314011 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of innate immune signaling and toll-like receptors in fibrosis and systemic sclerosis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015 Jan;17(1):474. doi: 10.1007/s11926-014-0474-z. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25604573 Review.
References
-
- De Minicis S., Rychlicki C., Agostinelli L., Saccomanno S., Trozzi L., Candelaresi C., Bataller R., Millán C., Brenner D. A., Vivarelli M., Mocchegiani F., Marzioni M., Benedetti A., Svegliati-Baroni G. (2013) Semaphorin 7A contributes to TGF-β-mediated liver fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 183, 820–830 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedman S. L. (2004) Stellate cells. A moving target in hepatic fibrogenesis. Hepatology 40, 1041–1043 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

