Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults
- PMID: 24448973
- PMCID: PMC4470349
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub3
Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults
Update in
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 7;6(6):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 22;2:CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub5. PMID: 31173647 Free PMC article. Updated.
Abstract
Background: Accurate, rapid detection of tuberculosis (TB) and TB drug resistance is critical for improving patient care and decreasing TB transmission. Xpert® MTB/RIF assay is an automated test that can detect both TB and rifampicin resistance, generally within two hours after starting the test, with minimal hands-on technical time. The World Health Organization (WHO) issued initial recommendations on Xpert® MTB/RIF in early 2011. A Cochrane Review on the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF for pulmonary TB and rifampicin resistance was published January 2013. We performed this updated Cochrane Review as part of a WHO process to develop updated guidelines on the use of the test.
Objectives: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF for pulmonary TB (TB detection), where Xpert® MTB/RIF was used as both an initial test replacing microscopy and an add-on test following a negative smear microscopy result.To assess the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF for rifampicin resistance detection, where Xpert® MTB/RIF was used as the initial test replacing culture-based drug susceptibility testing (DST).The populations of interest were adults presumed to have pulmonary, rifampicin-resistant or multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB), with or without HIV infection. The settings of interest were intermediate- and peripheral-level laboratories. The latter may be associated with primary health care facilities.
Search methods: We searched for publications in any language up to 7 February 2013 in the following databases: Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register; MEDLINE; EMBASE; ISI Web of Knowledge; MEDION; LILACS; BIOSIS; and SCOPUS. We also searched the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) and the search portal of the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform to identify ongoing trials.
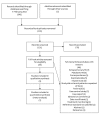
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials, cross-sectional studies, and cohort studies using respiratory specimens that allowed for extraction of data evaluating Xpert® MTB/RIF against the reference standard. We excluded gastric fluid specimens. The reference standard for TB was culture and for rifampicin resistance was phenotypic culture-based DST.
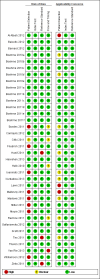
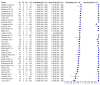
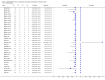
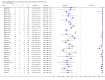
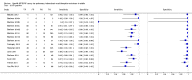
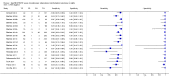
Data collection and analysis: For each study, two review authors independently extracted data using a standardized form. When possible, we extracted data for subgroups by smear and HIV status. We assessed the quality of studies using QUADAS-2 and carried out meta-analyses to estimate pooled sensitivity and specificity of Xpert® MTB/RIF separately for TB detection and rifampicin resistance detection. For TB detection, we performed the majority of analyses using a bivariate random-effects model and compared the sensitivity of Xpert® MTB/RIF and smear microscopy against culture as reference standard. For rifampicin resistance detection, we undertook univariate meta-analyses for sensitivity and specificity separately to include studies in which no rifampicin resistance was detected.
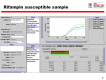
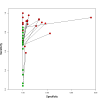
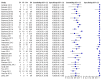
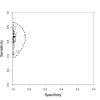
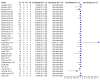
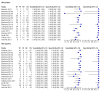
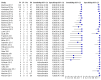
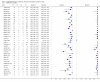
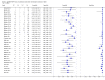
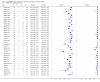
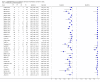
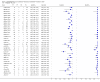
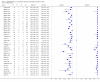
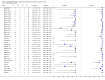
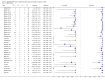
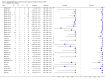
Main results: We included 27 unique studies (integrating nine new studies) involving 9557 participants. Sixteen studies (59%) were performed in low- or middle-income countries. For all QUADAS-2 domains, most studies were at low risk of bias and low concern regarding applicability.As an initial test replacing smear microscopy, Xpert® MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity was 89% [95% Credible Interval (CrI) 85% to 92%] and pooled specificity 99% (95% CrI 98% to 99%), (22 studies, 8998 participants: 2953 confirmed TB, 6045 non-TB).As an add-on test following a negative smear microscopy result, Xpert®MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity was 67% (95% CrI 60% to 74%) and pooled specificity 99% (95% CrI 98% to 99%; 21 studies, 6950 participants).For smear-positive, culture-positive TB, Xpert® MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity was 98% (95% CrI 97% to 99%; 21 studies, 1936 participants).For people with HIV infection, Xpert® MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity was 79% (95% CrI 70% to 86%; 7 studies, 1789 participants), and for people without HIV infection, it was 86% (95% CrI 76% to 92%; 7 studies, 1470 participants). Comparison with smear microscopy In comparison with smear microscopy, Xpert® MTB/RIF increased TB detection among culture-confirmed cases by 23% (95% CrI 15% to 32%; 21 studies, 8880 participants).For TB detection, if pooled sensitivity estimates for Xpert® MTB/RIF and smear microscopy are applied to a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients where 10% of those with symptoms have TB, Xpert® MTB/RIF will diagnose 88 cases and miss 12 cases, whereas sputum microscopy will diagnose 65 cases and miss 35 cases. Rifampicin resistance For rifampicin resistance detection, Xpert® MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity was 95% (95% CrI 90% to 97%; 17 studies, 555 rifampicin resistance positives) and pooled specificity was 98% (95% CrI 97% to 99%; 24 studies, 2411 rifampicin resistance negatives). Among 180 specimens with nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), Xpert® MTB/RIF was positive in only one specimen that grew NTM (14 studies, 2626 participants).For rifampicin resistance detection, if the pooled accuracy estimates for Xpert® MTB/RIF are applied to a hypothetical cohort of 1000 individuals where 15% of those with symptoms are rifampicin resistant, Xpert® MTB/RIF would correctly identify 143 individuals as rifampicin resistant and miss eight cases, and correctly identify 833 individuals as rifampicin susceptible and misclassify 17 individuals as resistant. Where 5% of those with symptoms are rifampicin resistant, Xpert® MTB/RIF would correctly identify 48 individuals as rifampicin resistant and miss three cases and correctly identify 931 individuals as rifampicin susceptible and misclassify 19 individuals as resistant.
Authors' conclusions: In adults thought to have TB, with or without HIV infection, Xpert® MTB/RIF is sensitive and specific. Compared with smear microscopy, Xpert® MTB/RIF substantially increases TB detection among culture-confirmed cases. Xpert® MTB/RIF has higher sensitivity for TB detection in smear-positive than smear-negative patients. Nonetheless, this test may be valuable as an add-on test following smear microscopy in patients previously found to be smear-negative. For rifampicin resistance detection, Xpert® MTB/RIF provides accurate results and can allow rapid initiation of MDR-TB treatment, pending results from conventional culture and DST. The tests are expensive, so current research evaluating the use of Xpert® MTB/RIF in TB programmes in high TB burden settings will help evaluate how this investment may help start treatment promptly and improve outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The CIDG provided funding in part for this review. KRS serves as Co‐ordinator of the Evidence Synthesis and Policy Subgroup of Stop TB Partnership's New Diagnostics Working Group. KRS received funding to carry out the original Cochrane Review from CIDG and McGill University and the updated Cochrane Review from the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), USA. MP is a recipient of a New Investigator Award from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and a salary award from Fonds de recherche du Québec ‐ Santé. MP serves as an external consultant for the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. CCB is employed by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) and has conducted studies and published on Xpert MTB/RIF as part of a collaborative project between FIND, a Swiss non‐profit, Cepheid, a US company, and academic partners. The product developed through this partnership was developed under a contract that obligated FIND to pay for development costs and trial costs and Cepheid to make the test available at specified preferential pricing to the public sector in developing countries. The authors have no financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the review apart from those disclosed. IS received funding to carry out the updated Cochrane Review from CIDG and USAID.
Figures




Update of
-
Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 21;(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub3. PMID: 23440842 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Al‐Ateah SM, Al‐Dowaidi MM, El‐Khizzi NA. Evaluation of direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in respiratory and non‐respiratory clinical specimens using the Cepheid Gene Xpert® system. Saudi Medical Journal 2012;33(10):1100‐5. - PubMed
-
- Balcells ME, García P, Chanqueo L, Bahamondes L, Lasso M, Gallardo AM, et al. Rapid molecular detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV‐infected patients in Santiago, Chile. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(10):1349‐53. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
-
- Alvarez‐Uria G, Azcona J M, Midde M, Naik PK, Reddy S, Reddy R. Rapid diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis in HIV‐infected patients. Comparison of LED fluorescent microscopy and the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay in a district hospital in India. Tuberculosis Research and Treatment 2012;Article ID: 932862:1‐4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen AB, Lillebæk T, Bang D, Prahl J. [Treatment and diagnostics of tuberculosis: moving slowly forward]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 2011;173(12):897‐9. - PubMed
-
- Bates M, O'Grady J, Maeurer M, Tembo J, Chilukutu L, Chabala C, et al. Assessment of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for diagnosis of tuberculosis with gastric lavage aspirates in children in sub‐Saharan Africa: a prospective descriptive study. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2013;13(1):36‐42. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
-
- GeneXpert MTB/RIF, a new tool for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in two municipalities in Brazil. Ongoing studyJanuary 2012.
-
- Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the rapid identification of TB and TB rifampin resistance in HIV‐infected and HIV‐uninfected patients with presumed pulmonary tuberculosis. Ongoing study 24 April 2012.
-
- A randomised control trial of sputum induction, and new and emerging technologies in a high HIV prevalence primary care setting. Ongoing studyAugust 2009.
Additional references
-
- Abimbola TO, Marston BJ, Date AA, Blandford JM, Sangrujee N, Wiktor SZ. Cost‐effectiveness of tuberculosis diagnostic strategies to reduce early mortality among persons with advanced HIV infection initiating antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2012;60(1):e1‐7. - PubMed
-
- Boehme CC, Nicol MP, Nabeta P, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, Tahirli R, et al. Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance: a multicentre implementation study. Lancet 2011;377(9776):1495‐505. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, et al. The STARD statement for reporting studies of diagnostic accuracy: explanation and elaboration. Clinical Chemistry 2003;49(1):7‐18. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

