Interleukin 6 mediates the therapeutic effects of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 24449042
- PMCID: PMC4365913
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1632
Interleukin 6 mediates the therapeutic effects of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
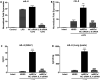
Adipose-derived stromal/stem cells (ASCs) have anti-inflammatory as well as immunosuppressive activities and are currently the focus of clinical trials for a number of inflammatory diseases. Acute lung injury (ALI) is an inflammatory condition of the lung for which standard treatment is mainly supportive due to lack of effective therapies. Our recent studies have demonstrated the ability of both human ASCs (hASCs) and mouse ASCs (mASCs) to attenuate lung damage and inflammation in a rodent model of lipopolysaccharide-induced ALI, suggesting that ASCs may also be beneficial in treating ALI. To better understand how ASCs may act in ALI and to elucidate the mechanism(s) involved in ASC modulation of lung inflammation, gene expression analysis was performed in ASC-treated (hASCs or mASCs) and control sham-treated lungs. The results revealed a dramatic difference between the expression of anti-inflammatory molecules by hASCs and mASCs. These data show that the beneficial effects of hASCs and mASCs in ALI may result from the production of different paracrine factors. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) expression in the mASC-treated lungs was significantly elevated as compared to sham-treated controls 20 hours after delivery of the cells by oropharyngeal aspiration. Knockdown of IL-6 expression in mASCs by RNA interference abrogated most of their therapeutic effects, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory properties of mASCs in ALI are explained, at least in part, by activation of IL-6 secretion.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Adipose-derived stromal/stem cell; Interleukin 6; Mouse.
© 2014 AlphaMed Press.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comparison of the therapeutic effects of human and mouse adipose-derived stem cells in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013 Jan 29;4(1):13. doi: 10.1186/scrt161. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23360775 Free PMC article.
-
Human multipotent stromal cells attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 6.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011 May 13;2(3):27. doi: 10.1186/scrt68. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21569482 Free PMC article.
-
Human mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing the IL-33 antagonist soluble IL-1 receptor-like-1 attenuate endotoxin-induced acute lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Oct;49(4):552-62. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0406OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23656573
-
Influence of type 2 diabetes and obesity on adipose mesenchymal stem/stromal cell immunoregulation.Cell Tissue Res. 2023 Oct;394(1):33-53. doi: 10.1007/s00441-023-03801-6. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Cell Tissue Res. 2023. PMID: 37462786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity: "priming" the lung for injury.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Aug;26(4):427-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 22449512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conditioned media from adipose stromal cells limit lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury, endothelial hyperpermeability and apoptosis.J Transl Med. 2015 Feb 21;13:67. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0422-3. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889857 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Mitophagy during Adipogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolated from Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) Horses.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jun 6;2018:5340756. doi: 10.1155/2018/5340756. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 29977307 Free PMC article.
-
Concise review: The obesity cancer paradigm: exploration of the interactions and crosstalk with adipose stem cells.Stem Cells. 2015 Feb;33(2):318-26. doi: 10.1002/stem.1857. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25267443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuro-Cells Mitigate Amyloid Plaque Formation and Behavioral Deficits in the APPswe/PS1dE9 Model of Alzheimer Disease While Also Reducing IL-6 Production in Human Monocytes.Cells. 2025 Jul 29;14(15):1168. doi: 10.3390/cells14151168. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801602 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of obesity on adipose-derived stromal cells and adipose tissue and their impact on cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022 Sep;41(3):549-573. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10063-1. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022. PMID: 35999486 Review.
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Dushianthan A, Grocott MP, Postle AD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Postgrad Med J. 2011;87:612–622. - PubMed
-
- Bonvillain RW, Zhang S, Eagle ME, et al. Battling Inflammation in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: Stem cell-based therapy targeting the root cause of acute lung injury. J Pulmonar Respirat Med. 2011;S2:001.
-
- Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179:1855–1863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

