Alk2 regulates early chondrogenic fate in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva heterotopic endochondral ossification
- PMID: 24449086
- PMCID: PMC4419363
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1633
Alk2 regulates early chondrogenic fate in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva heterotopic endochondral ossification
Abstract
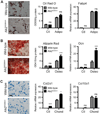
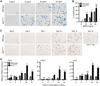
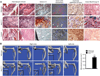
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling is a critical regulator of cartilage differentiation and endochondral ossification. Gain-of-function mutations in ALK2, a type I BMP receptor, cause the debilitating disorder fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) and result in progressive heterotopic (extraskeletal) endochondral ossification within soft connective tissues. Here, we used murine mesenchymal progenitor cells to investigate the contribution of Alk2 during chondrogenic differentiation and heterotopic endochondral ossification (HEO). Alk2(R206H/+) (gain-of-function), Alk2(CKO) (loss-of-function), and wild-type mouse embryonic fibroblasts were evaluated for chondrogenic potential. Chondrogenic differentiation was accelerated in Alk2(R206H/+) cells, due in part to enhanced sensitivity to BMP ligand. In vivo, Alk2(R206H/+) cells initiated robust HEO and recruited wild-type cell contribution. Despite expression of other type I BMP receptors (Alk3 and Alk6), chondrogenesis of Alk2(CKO) cells was severely impaired by absence of Alk2 during early differentiation. Alk2 is therefore a direct regulator of cartilage formation and mediates chondrogenic commitment of progenitor cells. These data establish that at least one effect of ALK2 gain-of-function mutations in FOP patients is enhanced chondrogenic differentiation which supports formation of heterotopic endochondral bone. This establishes ALK2 as a plausible therapeutic target during early chondrogenic stages of lesion formation for preventing heterotopic bone formation in FOP and other conditions.
Keywords: Alk2; Bone morphogenetic protein signaling; Chondrogenesis; Endochondral ossification; Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.
© 2014 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
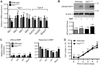
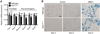
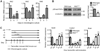
References
-
- Mackie EJ, Tatarczuch L, Mirams M. The skeleton: A multi-functional complex organ: The growth plate chondrocyte and endochondral ossification. J Endocrinol. 2011;211:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Forsberg JA, Potter BK. Heterotopic ossification in wartime wounds. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2010;19:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Cremin B, Connor JM, Beighton P. The radiological spectrum of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Clin Radiol. 1982;33:499–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

