Construction of synthetic nucleoli in human cells reveals how a major functional nuclear domain is formed and propagated through cell division
- PMID: 24449107
- PMCID: PMC3923965
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.234591.113
Construction of synthetic nucleoli in human cells reveals how a major functional nuclear domain is formed and propagated through cell division
Abstract
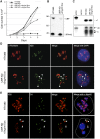
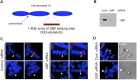
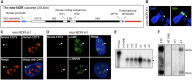
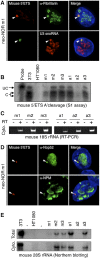
Human cell nuclei are functionally organized into structurally stable yet dynamic bodies whose cell cycle inheritance is poorly understood. Here, we investigate the biogenesis and propagation of nucleoli, sites of ribosome biogenesis and key regulators of cellular growth. Nucleolar and cell cycles are intimately connected. Nucleoli disappear during mitosis, reforming around prominent uncharacterized chromosomal features, nucleolar organizer regions (NORs). By examining the effects of UBF depletion on both endogenous NORs and synthetic pseudo-NORs, we reveal its essential role in maintaining competency and establishing a bookmark on mitotic NORs. Furthermore, we demonstrate that neo-NORs, UBF-binding site arrays coupled with rDNA transcription units, direct the de novo biogenesis of functional compartmentalized neonucleoli irrespective of their site of chromosomal integration. For the first time, we establish the sequence requirements for nucleolar biogenesis and provide proof that this is a staged process where UBF-dependent mitotic bookmarking precedes function-dependent nucleolar assembly.
Keywords: UBF; mitotic bookmarking; neo-NOR; nucleolar organizer region (NOR); nucleolus; pseudo-NOR.
Figures
Comment in
-
Driving nucleolar assembly.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 1;28(3):211-3. doi: 10.1101/gad.237610.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24493643 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Construction of synthetic nucleoli and what it tells us about propagation of sub-nuclear domains through cell division.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16):2501-8. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949124. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486191 Free PMC article.
-
Driving nucleolar assembly.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 1;28(3):211-3. doi: 10.1101/gad.237610.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24493643 Free PMC article.
-
The linker histone H1.2 is a novel component of the nucleolar organizer regions.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 16;293(7):2358-2369. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810184. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29301938 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudo-NORs: a novel model for studying nucleoli.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Nov;1783(11):2116-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.07.004. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18687368 Review.
-
Nucleolar organizer regions: genomic 'dark matter' requiring illumination.Genes Dev. 2016 Jul 15;30(14):1598-610. doi: 10.1101/gad.283838.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27474438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolar URB1 ensures 3' ETS rRNA removal to prevent exosome surveillance.Nature. 2023 Mar;615(7952):526-534. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05767-5. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Nature. 2023. PMID: 36890225
-
NORs on human acrocentric chromosome p-arms are active by default and can associate with nucleoli independently of rDNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 12;117(19):10368-10377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001812117. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32332163 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear organization mediates cancer-compromised genetic and epigenetic control.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Aug;69:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 9. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 29759441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emergent microenvironments of nucleoli.Nucleus. 2024 Dec;15(1):2319957. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2319957. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Nucleus. 2024. PMID: 38443761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the nucleolar responses to DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 25;48(17):9449-9461. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa713. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32857853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albert B, Colleran C, Leger-Silvestre I, Berger AB, Dez C, Normand C, Perez-Fernandez J, McStay B, Gadal O 2013. Structure–function analysis of Hmo1 unveils an ancestral organization of HMG-box factors involved in ribosomal DNA transcription from yeast to human. Nucleic Acids Res 41: 10135–10149 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belin S, Hacot S, Daudignon L, Therizols G, Pourpe S, Mertani HC, Rosa-Calatrava M, Diaz JJ 2010. Purification of ribosomes from human cell lines. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 49: 3.40.1–3.40.11 - PubMed
-
- Boisvert FM, van Koningsbruggen S, Navascues J, Lamond AI 2007. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 574–585 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
