Spatial control of phospholipid flux restricts endoplasmic reticulum sheet formation to allow nuclear envelope breakdown
- PMID: 24449268
- PMCID: PMC3909786
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.230599.113
Spatial control of phospholipid flux restricts endoplasmic reticulum sheet formation to allow nuclear envelope breakdown
Abstract
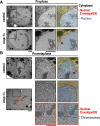
The nuclear envelope is a subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here we characterize CNEP-1 (CTD [C-terminal domain] nuclear envelope phosphatase-1), a nuclear envelope-enriched activator of the ER-associated phosphatidic acid phosphatase lipin that promotes synthesis of major membrane phospholipids over phosphatidylinositol (PI). CNEP-1 inhibition led to ectopic ER sheets in the vicinity of the nucleus that encased the nuclear envelope and interfered with nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD) during cell division. Reducing PI synthesis suppressed these phenotypes, indicating that CNEP-1 spatially regulates phospholipid flux, biasing it away from PI production in the vicinity of the nuclear envelope to prevent excess ER sheet formation and NEBD defects.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum; lipin; phosphatidylinositol; phospholipid synthesis.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
